状语从句用法讲解和练习

状语从句专题
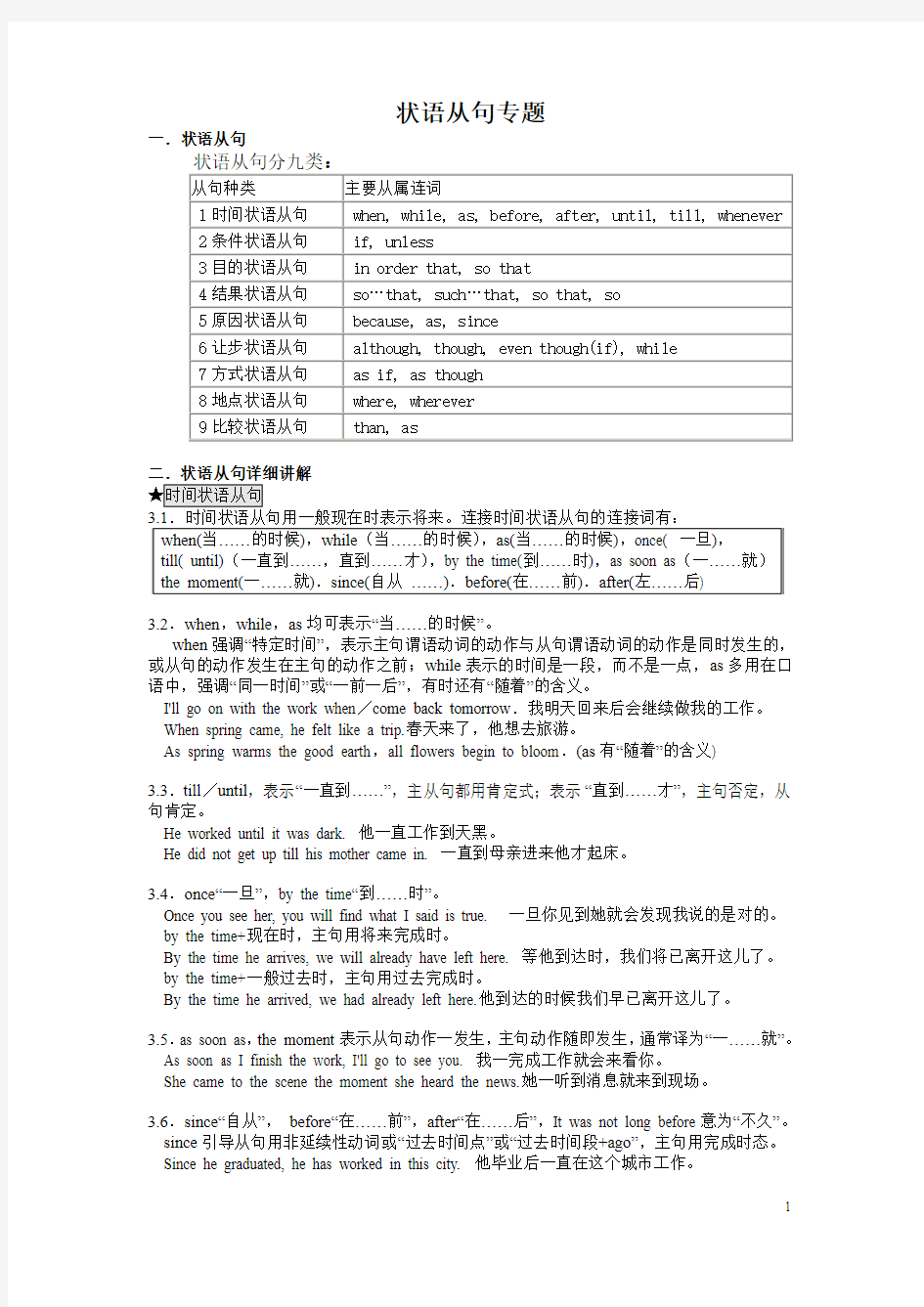
一.状语从句
3.2.when,while,as均可表示“当……的时候”。
when强调“特定时间”,表示主句谓语动词的动作与从句谓语动词的动作是同时发生的,或从句的动作发生在主句的动作之前;while表示的时间是一段,而不是一点,as多用在口语中,强调“同一时间”或“一前一后”,有时还有“随着”的含义。
I'll go on with the work when/come back tomorrow.我明天回来后会继续做我的工作。When spring came, he felt like a trip.春天来了,他想去旅游。
As spring warms the good earth,all flowers begin to bloom.(as有“随着”的含义)
3.3.till/until,表示“一直到……”,主从句都用肯定式;表示“直到……才”,主句否定,从句肯定。
He worked until it was dark. 他一直工作到天黑。
He did not get up till his mother came in. 一直到母亲进来他才起床。
3.4.once“一旦”,by the time“到……时”。
Once you see her, you will find what I said is true. 一旦你见到她就会发现我说的是对的。by the time+现在时,主句用将来完成时。
By the time he arrives, we will already have left here. 等他到达时,我们将已离开这儿了。by the time+一般过去时,主句用过去完成时。
By the time he arrived, we had already left here.他到达的时候我们早已离开这儿了。
3.5.as soon as,the moment表示从句动作一发生,主句动作随即发生,通常译为“一……就”。As soon as I finish the work, I'll go to see you. 我一完成工作就会来看你。
She came to the scene the moment she heard the news.她一听到消息就来到现场。
3.6.since“自从”,before“在……前”,after“在……后”,It was not long before意为“不久”。since引导从句用非延续性动词或“过去时间点”或“过去时间段+ago”,主句用完成时态。Since he graduated, he has worked in this city. 他毕业后一直在这个城市工作。
I haven't seen him since last year/ three years ago. 去年以来/3年来,我没见过他。
选出最佳答案
1) ____________ he was listening to the music, John fell asleep.
A. After
B. Before
C. While
D. As soon as-
2) How did you try to get to school on time _____________ you missed the school bus.
A. when
B. how
C. why
D. that
3) He was riding to school ______________ he was hit by a car this morning.
A while B. when C. as D. so
4) Lucy knew nothing about it _____________ her sister told her.
A. because
B. until
C. if
D. since
5) The policeman asked the child ____________ cross the street _____________ the traffic
lights turned green.
A. not; when
B. don't; before
C. not to; until
D. not to; since
6) The book was so interesting that he had read it for three hours he realized
it.
A. when
B. after
C. until
D. before
7) _____________ we had seen all the animals, we went home.
A. Then
B. After
C. Though
D. While
8) She has made many friends ______________ she came to our school.
A. before
B. after
C. since
D. until
9) — How long has the weather been like this?
A. Until last night
B. Ever since last night
C. Two days ago
D. Two days later
10) My uncle went to Australia last year. We haven't seen him .
A. since almost a year
B. from almost a year on
C. after almost a year
D. since almost a year ago
11) He was so tired that he fell asleep_______________he went to bed.
A. as if
B. even though
C. ever since
D. as soon as
12) I knew nothing about the accident _____________ my friend told me yesterday.
A. because
B. since
C. until
D. after
13) I didn't manage to do it ______________ you had explained how.
A. until
B. since
C. while
D. after
If you don't look after young trees, they will die very quickly.
If the museum charges for entry, a lot of people won't be able to visit it.
3.表示否定的条件用unless( =if...not)“除非,如果不”。
I shall not go to the cinema unless I finish my homework before eight.
说明:i f…not常可以用unless替代。
If you don?t study hard, you will fail in the exam.
You will fail in the exam unless you study hard.
4.表示使某事成为现实必要的条件用on condition that“条件是”,as long as ……只要”。
You may go swimming on condition that you don't swim too far away from the river bank.
As long as you don't study hard, you will fail in the exam.
5.祈使结构表条件。
前半部分的祈使结构相当于if条件句,可用动词或名词开头;后半部分的简单句常用一
地球。
=If you give me somewhere to stand, I will move the earth.
One more word, and I'll turn you out. 你再多说一句,我就把你赶出去。
=If you speak one more word, I will turn you out.
Use your head, then you'll find a way. 动动脑子你就能找到办法。
=If you use your head, you'll find a way.
试。
= If you don't work harder, you will never pass the exam.
Stop telling lies, or you will be punished. 如果你继续说谎,就会受到惩罚。
= If you don't stop telling lies, you will be punished.
选择最佳答案填空
1) — Would you like to go to the park with me, Susan?
— I'd like to, _____________ you don't want to go
alone.
A. until
B. before
C. if
D.
after
2) Tomorrow we'll go to the city park _____________ it is sunny.
A. as soon as
B. when
C. if
D. as
3) All of us will be happy ______________ y ou can come with us.
A. while
B. if
C. but
D. or
4) Nobody can learn English well _______________ y ou work hard on it.
A. if
B. unless
C. when
D.
but
5) The sports meet will continue it rains this afternoon.
A. if
B. since
C. as soon as
D.
unless
why,语气最强。He is absent today because he is ill. 他今天缺席,因为他病了。
I didn't go out because I was busy with homework. 我没有出去,因为我忙于家庭作业。
有时,可用because of后接名词或代词表示原因,此时because of=for(介词)。
We won't be able to come because of the weather. 由于天气的原因,我们来不了。
She was looking all the better for her stay in hospital. 她因为待在医院,显得好多了。
2) for意为“因为”,引导的从句并不说明主句行为发生的直接原因,只提供补充说明,且不可位于主句前。for前往往用逗号或分号与主句分开,引起的从句对主句加以解释。
I didn't go to see him, for a heavy snow was falling. 我没有去看他,因为在下大雪。
The days were short, for it was now December. 白天短了,因为现在已经是十二月了。
We must begin planning now, for the future may bring unexpected changes.
我们必须现在就开始筹划,因为将来可能会发生意想不到的变化。
有时,for引起的从句并不表示原因,而是表示一种推断或解释,而because则不能。Someone in the house must be ill, for a doctor has just come out.房子里一定有人病了,因为有个医生刚刚出来。
3) since意为“既然”、“由于”,一般表示对方已知的、无需加以说明的既成事实的理由(如果从句表示的原因不是确定的事实,就不能用since,通常用because)。
Since you are going, I will go too. 既然你要走,我也走了。
Since you are ill, I'll go alone. 由于你病了,我就一个人走了。
4) as意为“由于”,表示十分明显的原因,一般说明因果关系,着重点在主句,语气较弱。As it is snowing, we shall not go to the park. 由于正在下雪,我们就不去公园了。
He had to apologize, as he knew he had made a mistake. 他必须道歉,因为他知道他错了。
由as表示的原因语势最弱,常用于口语。
5) now that意为“既然”,有时可将that省去,含义与since接近。区别在于:since表示原先已存在的情况,而now that表示现在才发生的情况。
Now that it has stopped raining, let's start at once. 既然现在雨停了,咱们马上开始吧!Now that you have come, you may as well stay. 既然来了,你最好还是待在这儿。
2.地点状语从句
Put it where you can see it.
I'll find him, wherever he is. 不管他在哪里我都要找到他。
You should put the book where it was.你应该把书放在原来的地方。
Wherever you go, you should do your work well. 不论你到哪里都要把工作做好。
选择最佳答案
1) I hope to go to France some day _____________ there are many famous museums there.
A. though
B. unless
C. because
D.
where
2) — Would you like to go to the concert with me?
— I'd love to, ___________ I can't. ____________ I have a lot of homework to do.
A. and; Because
B. but; Because
C. so; And
D.
and; so
3) Jim has been in the factory for two years____________ he left school.
A. when
B. since
C. as soon as
D.
whether
4) Jack was very tired _____________ he played tennis all afternoon.
A. if
B. as soon as
C. because
D.
before
5) You'd better come back earlier ______________it is getting colder.
A. as
B. and
C. but
D.
or
6) Jane wore a raincoat _____________ it was raining.
A. so
B. but
C. however
D.
because
7) The Italian boy was regarded as a hero _____________ he gave his life for his country.
A. according to
B. because of
C. on account of
D.
because
2.although/though“虽然”。
Although I didn?t know anybody at the party, I had a very good time. 虽然晚会上的客人我一个也不认识,但我玩得很愉快。
[注意]“although…but”是个典型的错误,因为but是并列连词,不能与从属连词although 连用。但是,although可与yet,still连用,因为yet,still是副词,它可使前后关系更明确。3.while意为“然而”。
1) while用于对照,说明两种情况相反,意为“然而,但是”。
Tom is very outgoing, while Jane is shy and quiet.汤姆性格外向,而简却腼腆安静。
While I was reading, he was playing. 我在读书,而他在玩。
2) while意为“虽然,尽管”,同although,此时从句和主句的主语往往为同一人或物。While she liked cats。she never let them come into her room.虽然她喜欢猫,但她从不让猫进她的房间。
4.even if “即使”(if后陈述的是假设);even though“尽管”(though后陈述的是事实)。
I'm going to apply for the job, even if it pays very little. 即使报酬不高,我也要去申请那份工作。
He is an honest man, I say, even though I have opposed him. 我说他是个诚实的人,尽管我反对过他。
5.whether…(or not)“无论是……或是……”.
Whether it rains or not, I shall go out for an outing. 无论是否下雨,我都要外出游玩。Whether we win or lose, we are going to do our best. 无论胜败,我们都会尽最大努力。
[注意] whether作“无论”解,用现在时表将来;whether作“是否”解时则不能。
They'll go out whether it rains or not tomorrow. 无论明天是否下雨,他们都要出去。
Can you tell me whether it will rain or not tomorrow? 你能告诉我明天是否下雨吗?
It has the same result no matter which way you do it. 无论用什么方法来做,结果都一样。No matter how cold it is, she often goes swimming.无论有多冷,她总是常去游泳。
选择最佳答案填空
1) _____________ he's old, he can still carry this heavy bag.
A. Though
B. Since
C. For
D. So
2) — How do you like the concert given by the "Foxy Ladies"?
—Exciting, ______________one piece of the music wasn't played quite well.
A. so
B. though
C. because
D. and
3) — Shall we go on working?
—Y es, _____________ I prefer to have a rest.
A. when
B. if
C. because
D. though
4) Doctor Li went to see the patient _____________ it was raining heavily.
A. because
B. and
C. since
D. though
5) — This dress was last year's style.
—I think it still looks perfect _____________ it has gone out this year.
A. so that
B. even though
C. as if
D. ever since
6) No matter ____________ busy he is, he won't give up his hobby.
A. where
B. how
C. what
D. who
7) I never seem to lose any weight, ____________ hard I try.
A. even though
B. no matter how
C. as if
D. ever since
8) No matter ____________ you come, you are welcome.
A. how
B. where
C. when
D. what
9) Though it's raining, ______________ are still working in the fields.
A. they
B. but they
C. and they
D. so they
10) Nobody believed him _______________ w hat he said.
A. even though
B. in spite
C. no matter
D. contrary to
11) _____________what may happen, I won't change my mind.
A. Even if
B. Although
C. Perhaps
D. No matter 目的、结果、比较状语从句
【经典剖析】
1
以in order that,so that
can/ could或will/would加动词构成。
He works hard in order that he can serve his country well. 他努力工作,目的是为了能更好地为国家服务。
They started early so that they might arrive in time. 他们很早出发,以便按时到达。
[注意]“for+动名词”不用于表目的,但“for+名词”可用于表目的。
Write it in simple English to make(不能用for making) everybody understand. 为了能让每个人都理解,请用简单的英语写。
Better get up early for the early train. 为了能赶上早班火车,请早一点起床。
他做了个错误的决定,以至于他丢失了一半的财产。
The box is so heavy that nobody can move it. 这个箱子是如此重,(以至于)无人能移动它。It is such a heavy box that nobody can move it. 这个箱子如此重,(以至于)无人能移动它。[注意]so that既可引导目的状语从句,又可引导结果状语从句,其区别在于:引导结果状语从句时通常用逗号同主句分开。
3
We walked as fast as we could. 我们尽可能地快步行走。
The work is not so easy as you thought. 这工作没有你想的那么简单。
Nothing is so precious as health没有什么能像健康一样珍贵。
The harder you study, the greater progress you will make. 你越努力学习,进步就越大。
针对性练习
1.选择最佳答案填空:
1) I'll leave him a note _____________ he'll know where we are.
A. so that
B. so as
C. in order
D.
for
2) The question was _____________ difficult that nobody could answer ______________ .
A. very; them
B. very; it
C. so; them
D. so;
it
3) Mike is ______________ boy that we all like him.
A. a good so
B. so good a
C. a such good
D.
such good a
4) They were ____________ busy studying ______________ they couldn't go to the
restaurant with us.
A. so; that
B. such; as
C. very; that
D.
enough; as
5) It was _______________ t hat he had to ask for help.
A. so difficult work
B. so difficult a work
C. such a difficult work
D. such a difficult job
6) He started early _______________ he could get there before nine.
A. in order that
B. because
C. so as to
D. in
order to
7) Robert is good at languages, ________________ we all know.
A. because
B. for
C. as
D.
since
8) It looks _______________ it's going to rain.
A. that
B. as
C. as if
D.
that
【Keys】1) C 2) A 3) B 4) B 5) A 6) D 7)B 8) C 9) B 10) D 11) D 12) C 13) A 【Keys】1) C 2) C 3) B 4) B 5) D
【Keys】
1) C 2) B 3) B 4) C 5) A 6) D 7) D
【Keys】
2. 1) A 2) B 3) D 4) D 5) B 6) B 7)B 8) C 9) A 10) C 11) D
【Keys】
1. 1) in order that 2) so that 3) so... that 4) so... that 5) such... that
2. 1)A 2) D 3) B 4) A 5) D 6) A 7) C 8) C
比较状语从句讲解和练习题
比较状语从句: 状语从句指句子用作状语时,起副词作用的句子。比较状语从句是其中的一种,主要运用于形容词和副词的原级、比较级及最高级的句子之中。原级:as…as (和……一样),not so(as)…as …(和不一样);比较级:more…than(更);最高级:The most…in/of, the + 形容词+est…of/in。常用引导词:as(同级比较),than(不同程度的比较);特殊引导词:the more … the more … ;just as …,so…;A is to B what /as X is to Y;no … more than;not A so much as B。 比较状语从句通常由as或than引起,这类从句和大多数状语从句不同,它们不修饰动词,而是修饰as,so,less,more等副词,或其他比较级的词,如taller, harder.在这里讨论它们,不是作为动词修饰语,而是作为一种状语从句。包含这类从句的句子通常为L,即从句在后:She is as tall as I(or me). He works as hard as his brother(does). He does not work as hard as his brother. He does not work so hard as his brother. No other men work as(or so) hard as his brother (does).No other men work as hard as does his brother. She is taller than I(or me). She is taller this year than(she was tall)last year. She is more shy than unsocial. She thinks more about her appearance than(she thinks about)her personality. She finds it easier to read than to write. She is not taller than I.(Both are tall.) She is no taller than I.(Both are short.)注意这两句话的区别。 I cannot persuade him any more than your persuade a pillar.(= I am unable to persuade him,just as you are unable to persuade a pillar.) I can forget her no more than she(forgets)me. Nothing is more dangerous than that you (should)make friends with him. I will help you rather than that you(should)have any trouble.rather than 而不是…
状语从句用法讲解和练习汇编
第章状语从句 学习指导 状语从句在句子中作状语,用来修饰主句或主句的谓语。一般可分为九大类,分别表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、比较和方式。尽管种类较多,但由于状语从句与汉语结构和用法相似,所以理解和掌握它并不难。状语从句的关键是要掌握引导不同状语从句的常用连接词。现分别列举如下: 状语从句分九类: 在这一章节的学习中,要求同学们掌握各类状语从句基本概念,并能够灵活应用 第一节时间状语从句 1. 时间状语从句用一般现在时表示将来。连接时间状语从句的连接词有: 2. when,while,as均可表示当.... 的时候” when强调特定时间”表示主句谓语动词的动作与从句谓语动词的动作是同时发生的, 或从句的动作发生在主句的动作之前;while表示的时间是一段,而不是一点,as多用在口 语中,强调同一时间”或一前一后”有时还有随着”的含义。 I'll go on with the work when / come back tomorrow .我明天回来后会继续做我的工作。 When spring came, he felt like a trip.春天来了,他想去旅游。 As spring warms the good earth,all flowers begin to bloom . (as 有随着”的含义) as, when, while 都表示主、从句的动作或状态同时发生,但三者也有区别。as和when引导的从句既可表示一点时间,也可表示一段时间,从句中的谓语动词既可以是持续性动词,也可以为短暂性动词,经常可以互换使用;while引导的从句通常表示一段时间,从句中宜 用持续性动词作谓语。当从句中的谓语动词为持续性动词时,这三者可以通用(前面例句中 已有体现),再如: Mother was worried because little Alice was ill, especially as / when / while father was away in France. 妈妈担心,因为小艾丽思病了,特别是当父亲远在法国的时候。 如果从句和主句要表示一个人的两个动作交替进行或同时完成时,则多用as,可译为“一
状语从句语法讲解
咼中英语状语从句 定义: 在句中作状语的从句是状语从句,修饰主句中的动词、形容词或副词等.状语从句由从属连词引导,从属连词在句中不充当句子成分,只起连接作用,状语从句放在句首时,要用逗号,放在句 尾时不用. 分类 根据意义上的不同,状语从句可分为:①时间状语从句②地点状语从句③原因状语从句④ 目的状语从句⑤条件状语从句⑥结果状语从句⑦让步状语从句⑧方式状语从句⑨比较 状语从句三、时间状语从句主句是一般将来时,时间状语从句用一般现在时表将来;主句是—过去将来时,从句用一般过去时表示过去将来时;主句是一般过去时忆:“主将 ,从句用一般过去时.记从现” (一)引导时间状语从句的连词有:As,whe n (whe never),before,after,as soo n as,un til (till),since,every time,once. | (二)、具体应用1)“while ”主、从句动作或状态同时发生.用while引导的从句用延续性 动词,常表示较长的时间或一个过程.记忆:While 后用进行时.While we were having supper, all the lights went out. Please kee p quiet while others are study in g」 While I was writing letters last night,he was watching TV. 2 )When 表示“就在”的时候", while 意为反而,可是,表示转折.One evening Beethoven was walking in a street,when he sudde niy stopped outside a little house. 3)When ever无论什么时候,随时 1.When ever some one throws in some rubbish,the truck p roduees a pi eee of music. 每当有人扔进一些垃圾时,它(汽车)就放一段音乐 2.When ever we' re in trouble,they will help us. 3.I go to the theatre, whe never I am free. https://www.wendangku.net/doc/279709662.html,e and see me whe never you want to.你随时来看我 4) till和until(表示"直到” ”)句首多用until | 1在肯定句中表示“直到”为止”,主句谓语动词要用延续性动词 I was wait ing un til/till he arrived. 2、在否定句中表示“直到,,才”主句谓语动词常用终止性动词,这时until和till常被before 替换. I did n' t leave till/un til she came back. 5) si nee:主句用完成时,从句用一般过去时,si nee引导的从句间或可用现在完成时 It is two years since I have studied En glish. 1.We have known each other si nee we were childre n. 2.We have bee n friends (ever sin ce) since we met at school. 3.It is ”(一段时间)+since+—般过去时态句子 It is two years since my sister married. I
状语从句讲解及练习
状语从句 在复合句中担任状语成分的从句称为状语从句,修饰主句的谓语动词,形容词或副词,状语 说白了就是修饰动作的词或句,也可以理解成修饰谓语的词或句。通常由副词、介词短语、 动词不定式、分词和从句等担当。例如: 1. Naturally, our grandparents were pleased to get our phone call. (副词 ) 2. We worked hard, from sunrise to sunset. (介词状短语 ) 3. To help my disabled aunt, I spend an hour working in her house every day. (不定式 ) 4. Seen from a distance, the farmhouse looked deserted. (过去分词 ) 5. I know how to light a camp fire because I had done it before .(原因状语从句) 状语的位置比较灵活,可以位于句首、句末或句中。enough 用作状语修饰形容词和副词时 必须后置。 状语从句主要用来修饰主句或主句的谓语。一般可分为九大类,分别表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、比较和方式。尽管种类较多,但由于状语从句与汉语结构和用法 相似,所以理解和掌握它并不难。状语从句的关键是要掌握引导不同状语从句的常用连接词 和特殊的连接词即考点。现分别列举如下: 1.时间状语从句 常用引导词: when, as, while, as soon as, while, before, after, since , till, until 特殊引导词: the minute, the moment, the second, every time, the day , the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner ? than, hardly ? when, scarcely ? when I didn ’ t realize how special my mother was until I became an adult. While John was watching TV , his wife was cooking. The children ran away from the orchard( 果园 ) the moment they saw the guard. No sooner had I arrived home than it began to rain. Every time I listen to your advice, I get into trouble. When , while, as 都可解释为“当```的时候”但侧重点有所不同。 1) When Eg: When I arrived home , I had a little rest. 注意点: when 从句的主语与主句主语相同,谓语动词是be 动词时,从句主语和be 可以省略。Eg: When (she was) walking along the street, she met her class teacher. 2) As As 除了表示“当```的时候”,还可表示为“一面``` 一面”,“随着” Eg: He sang as he danced.(一面 ```一面 ) You will grow wiser as you grow older.(随着) 3) While 表示“当 ``` 的时候” 强调主句的动作和从句的动作同时发生,从句一般用进行时, 从句动词必须是延续性动词。 Eg: While we were working, they were having a rest. While (they were) having a discussion, they got very confused. 注意点: while 有对比的含义,解释为“然而”。 eg: I prefer black tee, while he likes coffee. 1.until, not ? until 表示“直到 ```才” ,在肯定句中主句常用延续性动词;在否定句中主句常用短暂性动词。
高考状语从句讲解
状语从句 一、时间状语从句 1、when, while, as 和whenever when 表时间点,时间段 while 表时间段;有“而”的意思 as “当……”,“一边……一边”,“随着……” whenever 每当,无论什么时候 It is cold when it snows. While there is life, there is hope. While we were speaking, he was reading newspaper. Just as Mrs Richards was entering the dinning-room, there was a knock on the front door. As we age, we trade strength for ingenuity, speed for thoroughness, and passion for reason. 随着年龄的增长,我们用力量换来了机敏,以速度换来了严谨,以热情换来了理智。 注:1)when还可作并列连词,其意义为“那时,这时”,相当于and at this/that time。常用于下列句式: sb.was doing sth.when...某人正在干某事就在这时…… sb.was about to/ going to do sth.when...某人正打算干某事就在这时…… sb.body has just done sth.when...某人刚干了某事就在这时…… 2)如果主句表示的是短暂动作,而从句用延续性动词的进行时态表示在一段时间内正在进行的动作时,when,while 与as可互换使用。如: When/While/As I was walking down the street,I came across an old friend of mine. 2、before/ after It will be five years before we meet again.五年之后我们才能见面。 After you think it over, please let me know what you decide. After her husband had gone to work, she sent her children to school. 3、until, till, not...until 1)肯定句:主句的谓语是延续性动词,主从句均为肯定式,意为“某动作一直持续到某时间点才停止”
中考状语从句讲解及练习
状语从句 状语从句用来修饰主句中的动词,副词和形容词的从句叫状语从句。根据其含义状语从句可分为时间状语从句,地点状语从句,条件状语从句,原因状语从句,结果状语从句,比较状语从句,目的状语从句,让步状语从句。 1. 时间状语从句 (1)时间状语从句常用when, as, while, before, after, since, till, until, as soon as等连词来引导。例如:It was raining hard(rain hard 下大雨)when got to school yesterday. While he was doing his homework, the telephone rang. As he walked along(沿着走)the lake, he sang happily. He had learned a little Chinese before he came to China. After he finished middle school, he went to work in a factory. (2)在时间状语从句里,通常不用将来时态,用现在时态表示将来的动作或状态。例如: I’ll ring you up as soon as I get to New York. I will tell him everything when he comes back. He won’t believe it until he sees it with his own eyes. (3)在带有till或until引导的时间状语从句的主从复合句里,如果主句用肯定式,其含义是“一直到……时”,谓语动词只能用延续性动词。如果主句用否定式,其含义是“直到……才……”, “在……以前不……”, 谓语动词可用瞬间动词。例如: The young man read till the light went out(熄灭). Let’s wait until the rain stops. We won’t start until Bob comes. Don’t get off(从下来)until the bus stops. 【Till是指直到某一特定事件发生的时候,而在那个时刻之后,该事情或状况仍将持续。Until 是指直到某一特定事件发生的时候,而讲话的人在自己心里认为,在那个时刻之后,该事情或该状况将中止(不怎么可能持续)。固定组合里from morning till night,till/until是不能替换的,】2. 条件状语从句 (1)条件状语从句通常由if, unless引导。例如: What shall we do if it snows tomorrow? Don’t leave the building unless I tell you to. (2)在条件状语从句里,谓语动词通常用现在时态表示将来的动作或状态。例如: I’ll help you with your English if am free tomorrow. He won’t be late unless he is ill. (3)“祈使句+ and (or)+ 陈述句”在意思上相当于一个带有条件状语从句的复合句。例如:Hurry up, or you’ll be late. =If you don’t hurry up, you’ll be late. Study hard and you will pass the exam. =If you study hard, you will pass the exam. 3. 原因状语从句 (1)原因状语从句通常由because, since, as引导。例如: He didn’t come to school because he was ill. As it is raining, we shall not (不得;不应该)go the zoo. Since you can’t answer the question, I’ll ask someone else. (2)because表示直接原因,语气最强。Because引导的原因状语从句多放在主句之后。回答由why提出的问题,只能用because。As和since语气较弱,一般用来表示明显的原因。由as 和since引导的原因状语从居多放在句首。例如: ------Why aren’t going there?
状语从句讲解及习题附答案
(一)状语从句概述 定义状语从句用作状语,是起副词作用的句子。 位置状语从句可以放在主句之前,也可以放在主句之后,时间、条件、原因和让步状语从句放在句首时需要用 逗号和主句隔开。 分类根据其作用可以分为时间、地点、原因、条件、目的、让步、方式和比较等状语从句。 作用它可以修饰谓语、非谓语动词、定语、状语和整个句子。 (二)状语从句详解 1. 时间状语从句 引导词用法示例 when 意为“当…的时候”。When 引导从句的谓语动词可以 是延续性动词,也可以是 瞬间动词。并且when有 时表示“就在那时”A liar is not believed when he speaks the truth.说谎者讲真话时也没有人相信。When he arrives, I’ll call you. When you laugh and smile, your body relaxes. while 意为“在…的时候,在…的 同时”。While引导从句的 谓语动词必须是延续性While I was standing at the window, I saw several boys running along the street.
的,发生时间较长,并强调主句和从句的动作同时发生(或者相对应)。While 有时还可以表示对比。While John was watching TV, his wife was cooking. as 意为“一边…一边…”。As 引导的动作是延续性的, 发生时间较短,一般用于 主句和从句动作同时发 生;as也可以强调一前一 后。The writer was angry as he was travelling on a train to London because someone had invaded his “space”. He smiled as he stood up. after 意为“在…之后”。表示主句 动作发生在从句动作之 后。主句与从句的动作时 间关系与before引导的从 句相反。With many hungry visitors waiting, don’t stay too long at your table after you have finished. If an early exit is necessary, you can leave after a scene is over. before 意为“在…之前”。引导的从 句不用否定形式的谓语, 并且当before引导的从句 位于主句之后,有时译成 “就,才”。当主句用将来时,You can’t watch TV before you finish your homework. Before it ended, the theatre was almost empty. My father had left for Canada
时间状语从句讲解和练习(答案)
时间状语从句 用句子表达一件事情或一个行为发生的时间,这个句子就叫时间状语从句。时间状语从句根据其所表示的时间不同,所使用的连词也不同。下面我们一起来看一下几个常见的时间状语从句: 1.when引导的从句:表示主句的动作和从句的动作同时发生,或从句的动作发生在主句动作之前。 例如:I was going out when a visitor came. (动词动作同时发生。)我正要出门,有客人来访。 I shall tell her the good news when she comes.她来时,我将告诉她这个好消息。 小试牛刀:I found mother cooking for me. I got home.(when)_______________________________________ He was listening to the radio when I home. (get) 2.while 引导的从句:表示“当……过程中”,强调某一段时间内主句和从句中谓语动词所表示的动作在同一时期发生。由于while从句表示一个持续的行为,所以从句中要用持续性动词,并且持续性动词常用进行时态。例如:Keep an eye on my little sister while I am away.我不在时,请照看一下我的小妹妹。 While we were watching TV, Jim came in. 我们看电视的时候,Jim进来了。 小试牛刀:It started to rain. We were playing football.(while)_______________________________________ Lucy was cleaning the room Lily was listening to music. 3.as引导的时间状语从句:表示“当……的时候;一边……一边……;随着……”,其从句的主语与主句的主语往往是同一人或物。 例如:She sang as she worked. 她一边工作一边唱歌。=She was singing as she was working. I saw him as he was getting off the bus. 正当他下公共汽车时, 我看见了他。 小试牛刀:we walked, we talked. You will grow wiser you grow older. 4.before引导的从句:一般表示主句的动作发生在从句动作之前。 例如:I didn’t know any English before I came here. 我到这儿来之前,一点英语都不懂。 例如:I had written my report before my father came back. 小试牛刀:He bought the ticket he went to see the film. 5.after引导的从句:表示主句的动作发生在从句动作之后。 例如:After he locked the door, he left. 他锁上门后,就走了。 After he had finished his work, he played a game of chess with his friend. 他做完工作后,和朋友下了一盘棋。小试牛刀:I will go out to play basketball with you. I finish my homework.(after) _______________________ _ He left the classroom he had finished his homework the other day. 6.since引导的从句:表示“自从……以来”,从句中的动词一般表示动作的起点,用过去时。主句中的动词表示动作延续的情况,一般用现在完成时。如果主句中的动词表示的不是延续的动作而是表示目前的状态,可用一般现在时。 例如:Since he met this good friend, he has made great progress in his studies. 自从遇见了这个好朋友,他已在学习上取得了巨大的进步。 例如:It is twenty years since she joined the Party. 她入党二十年了。(主句中的动词表示的是状态,用现在时。)小试牛刀:it is five years since we last time.(meet) Mr green has taught in that school since he (come) to China three years ago. 7.until 引导的从句:表示一个动作持续到某一时刻。 (1)表示“直到……”,如果主句中的谓语动词是延续性动词时,用肯定或否定形式都可以,但表达的意思不同。(2)表示“直到……才”,主句用否定式,从句用肯定。如果主句中的谓语动词是瞬间动词时,必须用否定形式。
状语从句讲解和练习
状语从句 状语从句修饰主句/主句的谓语。一般有九大类:表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、比较和方式等。 时间状语从句 1. 用when引导:when表示“当……时候”。如: Things were different when I was a child. 我小时候情况与现在不同。 People breathe more slowly when they are asleep. 人睡觉时呼吸比较缓慢。 2. 用while引导:while表示“当……时候”。如: We must strike while the iron is hot. 我们要趁热打铁。 I went swimming while the others played tennis. 我去游泳,其余的人都打网球去了。 注意:while 所引导的时间状语从句中谓语动词必须是持续性的,不能是短暂性的。 3. 用as引导:as表示“当……时候”“随着”。如: He dropped the glass as he stood up. 他站起来时,把杯子摔了。 We get wiser as we get old. 随着年岁的增长,我们也变得聪明些了。 4. 用before引导:before表示“在……之前”。如: Turn off the lights before you go to bed. 睡觉前要关灯。 Before he went to university he was a worker. 上大学之前他是工人。 5. 用after引导:after表示“在……之后”。如: I will tell you after they leave. 他们走我再告诉你。 After you finish the letter show it to me.信写完后给我看看。 6. 用until / till引导:until / till表示“直到……”。如: He waited until she was about to leave. 他等着一直到她准备离开。 I watched him until he disappeared in the distance. 我瞧着他直到他在远处消失。 这类句型的主句动词通常只能是延续性动词,不能是终止性动词。但是,在否定句中,主句动词可以是终止性动词,此时构成not…ntil [till]…句式,意为“直到……才……”。如:
高中英语状语从句讲解和练习(含答案)之欧阳语创编
状语从句讲解和练习状语修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。通常由副词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词和从句等担当。例如:1. Nat urally , our grandparents wer e pleased to get our phone call . (副词)2. We worked ha rd , from sunrise to sunset . (介词状短语)3. To help my d isabled aunt , I spend an ho ur working in her house ever y day . (不定式)4. Seen from a distance , the farmhouse l ooked deserted . (过去分词)
5. I know how to light a ca mp fire because I had done it before .(原因状语从句)状语的位置比较灵活,可以位于句首、句末或句中。enough用作状语修饰形容词和副词时必须后置。 状语从句主要用来修饰主句或主句的谓语。一般可分为九大类,分别表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、比较和方式。尽管种类较多,但由于状语从句与汉语结构和用法相似,所以理解和掌握它并不难。状语从句的关键是要掌握引导不同状语从句的常用连接词和特殊的连接词即考点。现分别列举如下:1.时间状语从句常用引导词:when, as, while, as soon as, while, before, after, since , ti ll, until特殊引导词:the minute, the moment, the sec ond, every time, the day,the instant, immediately , directly, no sooner … than, hardly …when, scarcely
状语的具体讲解(十)方式状语
句子成分之——-状语的具体讲解(十)方式状语 具体用法:方式状语 导读:方式状语,描述动作、事件或情况发生及存在的方式。其表达方式通常有: 1. 方式副词(介绍了常用副词) 2. 介词短语(区分了by,through, in, with四个表方式的介词用法) 3.形容词短语 4. 方式状语从句 (1)as if/as though (2)as/like (just) as…so…表示“正如”、“像……”。 (3)(in) the way (that) 引导的方式状语从句“以…方式” (一)方式副词,用来回答how 提出的问题。常见的此类副词主要有:angrily 生气地anxiously 焦急地badly 糟糕地 calmly 冷静地carefully 仔细地carelessly 粗心地 clearly 清晰地closely 紧密地dangerously 危险地 eagerly 热心地effectively 有效地faithfully 忠诚地 firmly 坚定地happily 高兴地nervously 紧张地 suddenly 突然地thoroughly 完全地uncomfortably 不舒适地 well 很好地widely 广泛地willingly 情愿地 方式副词,等于介词短语“in a +形容词+ way”。 例如:angrily 等于in an angry way Some Internet words are widely used and spread.有些网络语言被广泛地使用和传播。 Volunteers always help others eagerly.志愿者们总是热心地帮助他人。 Can you speak it clearly?你能清楚地讲一下它吗? A dog came out from behind the door suddenly.一只狗突然从门后跑了出来。 (二)介词短语,常见的有:in, by...,with..., through...等。 1. by的用法 (1)by+n/动词ing表示“通过……方式” The blind learn something by touching. 盲人通过触摸学习东西。
(完整)高中英语状语从句讲解及练习
状语从句 在复合句中作状语,位置灵活。 状语从句可分为时间状语从句,目的状语从句,条件状语从句,让步状语从句,地点状语从句,原因状语从句,方式状语从句,结果状语从句。 (一)时间状语从句 1.when, as, while a.when表时间,从句既可以用延续性动词,又可以用瞬间动词。 Eg: When I get there I will call you. 如果when引导的时状的主语与主句的主语相同,而从句的谓语又是be动词时,那么从句中的主语与be 可省。 Eg:When (you are)in trouble, you can ask her for help. 如果when引导的时状的主语与主句的主语相同时,往往可以用“when+分词”的形式代替该状从。Eg:When I came into the room(When coming into the room), I found the light was off. b.while表时间,从句需用延续性动词,或者主句的动作发生在从句的动作进行过程中。主句的谓语动词 通常是非延续性动词。 Eg: He came in while I was reading a book. I met her while I was in school. c. as表时间,与when相似,但侧重强调主从句动作同在时间点或同时间段进行。同时可表示主句的动作随着从句的动作的变化而变化。 Eg: He jumps as he sings. As the wind rose, the noise increased. 2.before(在……之前)与after(在……之后) Eg:See me before you leave. I saw them after I arrived. 3. till与until 肯定形式表示的意思是"做某事直至某时"。否定形式表达的意思是"直至某时才做某事"。 Eg: Wait till/untill I call you. 等着直到我叫你。 She didn't arrive till/until 6 o'clock.. 她直到6点才到 但是置于句首时只可用untill. Until you told me, I had heard nothing of what happened. 直到你告诉我以前,出了什么事我一点也不知道。否定形式有另外两种表达方式: (1)Not until …在句首,主句用倒装。 Man did not know what heat was until the early years of the 19th century. =Not until the early years of the 19th century did man know what heat was. (2)It is not until…that… He will not go to bed until his mother comes home. =It is not until his mother comes home that he will go to bed. 4. as soon as/the moment/the instant/the second/the minute/immediately和hardly/scarcely…when, no sooner…than a. as soon as/the moment/the instant/the second/the minute/immediately 表示主句和从句的动作同时发生。译为“一……就” Eg:As soon as she heard the news, she began crying. b. hardly/scarcely…when, no sooner…than都可以表示"一……就……"的意思,但主句谓语动词一般要用过去完成时,从句谓语动词要用一般过去时。 Eg:I had hardly / scarcely got home when it began to rain. I had no sooner got home than it began to rain.注意:如果hardly, scarcely 或no sooner置于句首,句子必须用倒装结构:Hardly / Scarcely had I got home when it began to rain. No sooner had I got home than it began to rain。 1. We called the First - Aid Center_______ the traffic accident happened. A. immediately B. shortly C.quickly D. hurriedly 2. The roof fell _____he had time to dash into the room to save his baby. A. before B. as C. after D. until 3. A good storyteller must be able to hold his listeners’ curiosity he reaches the end of the story. A when B whenever C.after D.until 4. I had just started back for the house to change my clothes _______ I heard the voices. A. as B. for C. while D.when 5. ______ the day went on, the weather got worse. 1
并列句和状语从句讲解.
并列句和状语从句讲解 一简单句 主语+谓 1 主语+Vt+宾语(动宾结构) 2 主语+Vt+宾语+宾补 3 主语+Vt+宾语(Sb)+宾语(Sb)(双宾语) 4 主语+Vi 5主语+Vi+介词+宾语(介宾) 6主语+系动词+表语(系表结构) 二并列句 1 表示递进 2 表示选择 3 表示转折 4 表示因果 三复合句 1 定语从句 2 名词性从句:主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句 3 状语从句:时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、方式、比较 一并列句 1 表示递进:and, not only…but also…,neither…nor…,not…but… 2 表示选择:or, either…or…,otherwise 就近原则:Neither he nor I am living here. Either he or I am living here. Not only he but also I am living here. 3 表示转折:but, yet, whereas, while 4 表示因果:so, as, for, because, since, now that 二状语从句 1 时间状语从句 (1)when, while, as (2)as soon as, immediately, instantly, directly, the moment, the minute, the instant, no sooner…than…,hardly/scarcely…when… The moment/Immediately I heard the voice, I knew Father was coming. No sooner had we arrived at the station than the train left. Hardly had we got home when it began to rain. (3)till, until, not…until(部分倒装,强调句) I didn’t know about it until you told me.
- 状语从句完整讲解和练习
- 状语从句讲解和练习题答案
- 高中英语状语从句讲解和练习(含答案)
- 状语从句讲解及习题附答案教学内容
- 比较状语从句讲解和练习题
- 高中英语状语从句讲解及练习[含答案解析]
- 状语从句讲解和练习PPT课件
- (完整版)比较状语从句讲解及精选练习(附答案)
- (完整版)状语从句讲解及练习题50题
- 状语从句讲解和练习(20200526003646)
- 时间状语从句讲解和练习(答案)
- 20XX状语从句用法讲解和练习
- 状语从句讲解及练习
- 比较、让步、地点状语从句讲解和练习(答案)
- 比较状语从句讲解及练习附答案
- 状语从句讲解和练习
- 状语从句讲解及练习题50题-有答案
- 初中状语从句讲解及习题附答案
- 状语从句讲解及练习.doc
- 状语从句课件讲解和练习
