英语6种时态专项教学导学案

英语6种时态专项教学导学案
【课前延伸】
请同学们认真讨论假期的经历和故事(注意时态)
【课内探究】
一、学习目标
1.学习掌握六种的时态构成,常用的时间状语以及用法(重点)
2.熟练综合运用所学习的六种时态。(难点)
3. 能运用所学时态谈论自己的日常生活。
二、预习检测
1. She often_____ (watch) TV on Sunday.
2. He ____________(not play) the guitar last week.
3. Tom_______ (read) an interesting book now.
4. He_________ (listen) to the radio when I came in.
5. I don’t know if it _______ (rain) tomorrow.
6. We ___________(be) good friends since we met at school.
【友情提示】请同学们自主归纳总结以上句子所运用的时态,小组讨论交流。
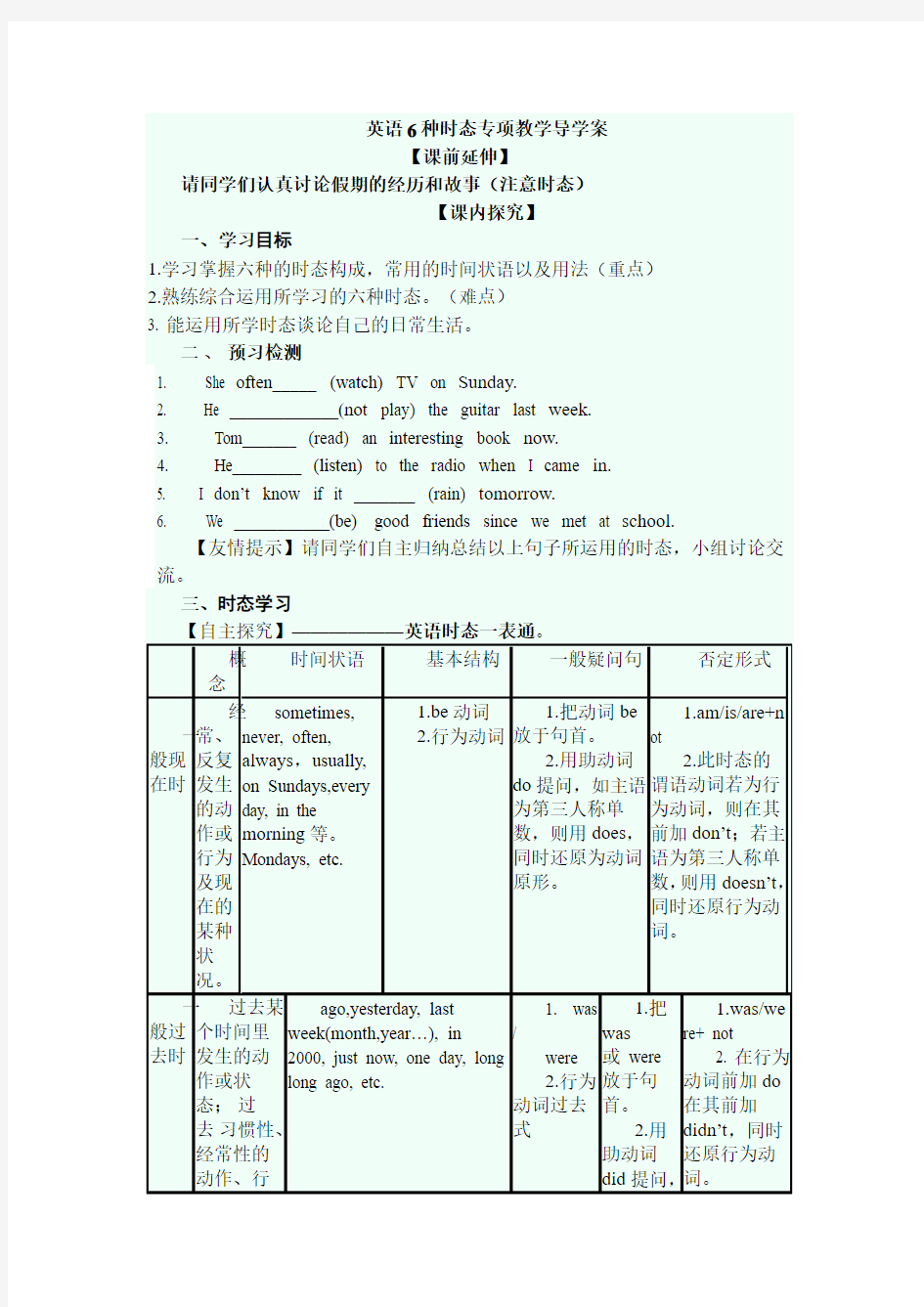
三、时态学习
【自主探究】——————英语时态一表通。
概
念
时间状语基本结构一般疑问句否定形式
一般现在时经
常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
sometimes,
never, often,
always,usually,
on Sundays,every
day, in the
morning等。
Mondays, etc.
1.be动词
2.行为动词
1.把动词be
放于句首。
2.用助动词
do提问,如主语
为第三人称单
数,则用does,
同时还原为动词
原形。
1.am/is/are+n
ot
2.此时态的
谓语动词若为行
为动词,则在其
前加don’t;若主
语为第三人称单
数,则用doesn’t,
同时还原行为动
词。
一般过去时过去某
个时间里
发生的动
作或状
态;过
去习惯性、经常性的
动作、行ago,yesterday, last
week(month,year…), in 2000, just now, one day, long long ago, etc.
1. was
/
were
2.行为
动词过去
式
1.把
was
或 were
放于句
首。
2.用
助动词
did提问,
1.was/we
re+ not
2. 在行为
动词前加do
在其前加
didn’t,同时
还原行为动
词。
为。同时还原
为动词原
形。
现在进行时表示现
阶段或说话时正在进行的动作或状态。now, at this time, these
days, etc.
am/ is/
are +doing
把be
动词放在
句首。
am/ is/
are +not
+doing
过去进行时表示过
去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的动作或行为。
then,at this time
yesterday,at that time,at that
moment yesterday,at 7
o’clock last night,以when引
导的谓语动词是一般过去
时的时间状语.。
was/
were+
doing
把
was或
were放在
句首。
was/
were+ not+
doing
一般将来时表示将
要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
tomorrow, the day after
tomorrow ,
n extday(week,month,year…)
,soon, in a few minutes(in +
一段时间), from now on ,
in the future等.
1.be
going
to+do
2.will
+do
1.be
放在句
首。2.will
提到句
首。
1.be
going to+
not+ do
2.will +
not+ do
现在完成时过去发
生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。already, yet, just,
ever,never,before, in the past few years, so far 等,及由for 或since引导的时间状语
Have/
has
+done
把
have或
has放在
句首。
have/ has
+not+ done
1.自主阅读时态列表,自主探究,掌握所学习时态,发现问题,小组交流。
2. 趁热打铁:看一看谁是时态小能手
? 1. Jim already ( clean )the classroom.
? 2. We (live )here for 3 years.
? 3. I ( cook ) when my mother came home yesterday.
? 4. John ( not do )homework on Sundays.
? 5. He ( do) his homework every day.
? 6. Li Lei ( write)to his father now.
? 7. They (have )a meeting just now.
3. 【中考链接】学生自主完成,发现问题,小组交流,反馈归纳
1)(2010·随州市)-Have you read this book? -Yes.I____ it two weeks ago.
A.is reading B.have read C.will read D.read
2)(2010.·攀枝花) Mary with her sisters_______ Chinese in China now.
A. are studying
B. have studied C is studying D was studying.
3)(2010.·宿迁)I_____ the charity show on TV when the telephone rang.
A. watch
B. watched
C. am watching
D. was watching
4)(2010·滨州)—Have you ever been anywhere for a trip?
-- A trip? I_____ away from my hometown even once.
A. went
B. have gone
C. have been D have never been
5)(2010.·江西)—Hello, Sandy. This is Jack. What are you doing?
-- I’m watching a match. It started at 7p.m. and ___on for another half an hour. A. has been B. was C had been D. will be
当堂检测,反馈纠正
一、基础题用所给单词的正确形式填空
1. Mike is from American. He _______(speak)English.
2. They ________(invite)her to the party, so she was very happy.
3. If it _______ (not rain) tomorrow, we_______ (go) for a picnic.
4. When we ______ (arrive) home yesterday evening, my mother _______ (watch) a wonderful football match..
5.Hurry up!They _____________ (wait) for you.
6. We ___________ (study) in this school for three years.
二、提高题用play填出短文中所缺的动词:
I often basketball after school. I it tomorrow. I it yesterday becaus e I was ill. But my friends ______ it at four yesterday afternoon. When I was 10, I (begin) to play it. Since then, I it for 5 years. But now what am I doing? I it, I’m writing my diary
【课后提升】
一.复习巩固本课时所学习的六种时态,小组检查反馈。
二.巩固作业:
1.冲刺中考读一读,选一选。(必做)
1) (2010.·潍坊)—Is Jessica giving us a speech this evening?
—No, it _________ be her.She _________ to Japan.
A.mustn't;has gone B.mustn't; has been
C.can't; has gone D.can't; has been
2) (2010.·潍坊)A moment, please.I'm checking if Mr. Smith _________
free tomorrow.
A.is B.being C.to be D.will be
3) (2010.·江苏) The teachers____________ the office for a few minutes w hen we arrived. We didn’t meet them.
A. had been away from
B. had left
C. have been away from
D. have left
4) (2010.·湖北)—When________ Jessy ________to New York?
—Yesterday.
A. does; get
B. did; get
C. has; got
D. had; got
5) (2010.·吉林) I bet Mrs. Black will come to help us with the
celebration if she ______ too busy tomorrow.
A. is
B. will be
C. won’t be
D. isn’t
2. Writing: (选做)My three days
要求:灵活运用所学习时态,描述你昨天已干的事情,某时正在干的事情,过去打算干的事情;经常干的事情,正在干的事情,现在已完成的事情,打算干的事情,相信你一定能够把你的生活描述的趣味无穷。
高中英语英语时态完整版
英语的时态
般现在时 一直以来的习惯动作;目前状态;规律 一般现在时J单三人称:动词r或es [非单三人称:动词原形
动词第三人称单数的变化规则 1>直接在动词后+S like- likes play-plays 2、以s, x, sh, ch,接尾時动词:+es wash-washes 3、以辅音+o接尾的动词:+es go-goes 4、以辅音+y接尾的动词:变y为i+es
fly-flies ?般现在时的用法 1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语everyday,often, always, once a week, seldom, usually等连用。 I leave home for school at 7 every morning. He cycles to work every day. 2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。 The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. Water boils at 100 centigrade degrees.
3)表示格言或警句中。 Failure is the mother of success. 失败是成功之母。 4)现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。 I don't want so much? Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.
1)伦love (Cove) sports. 2)Sfie sings (sin^) we(L 3)Tom andjofin _____ w atch (watc? TV every evening. 4)My son goes (g? to scfiooCby 6i忽. 5)teacherusualfy ______ walk帥瑚)to school 6)Tive plus two _____ m akes (ma同seven. 7)TJiey ad I ike 伍匍kirn. 8)加sun____ falls (faj in the west. 二、一般过去时
时态总结教学文档
一、一般现在时: 1.概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 2.时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, 3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要加(e)S) 4.否定形式:am/is/are+not;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 6.例句:. It seldom snows here. He is always ready to help others. Action speaks louder than words. 二、一般过去时: 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc. 3.基本结构:be动词;行为动词 4.否定形式:was/were+not;在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。 6.例句:She often came to help us in those days. I didn't know you were so busy. 三、现在进行时: 1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。 2.时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc.
高中英语时态教案
高中英语教案时态总结 一、时态的内涵 Tense翻译为时态,包含时间+状态两个方面。 时间的划分:过去,现在,将来 状态的划分:一般,进行,完成 状态——实意动词: 四种形式例:go, went, gone, going 四种形式各有分工一般:go, went 进行:going 完成:gone 例: 一般 I go to school every day. I went to school yesterday. 进行 we are learning English. I was learning English when you called me yesterday. 完成 We have had breakfast. I had had breakfast by 8 this morning. 时间——助动词 那接下来又有新的问题了。比如说,现在分词,它只有一种形式,如going ,或者learning, 那我们时间又不一样,有过去进行的,现在进行的,比如刚才的两个例句,we are learning English, 我们用的是are. I was learning English yesterday when you called me. 用的是was. 所以我们发现,learning是没有变化的,但前面这个are, was是变化的。它们的变化就把这个时间讲清楚了。而它呢,位于learning实意动词之前的这个,叫助动词。也就是说,be,是个助动词。如果我问be是什么词很多同学肯定会说be是系动词,其实be又是助动词,又是系动词,这里的be就是助动词。大家该如何理解呢,看这里,一个实意动词,只能把状态讲清楚,但因为一个状态里面,有不同的时间,比如进行,有过去进行,现在进行,和将来进行,而实意动词本身不能把这个时间讲清楚,于是就借助于,求助于,助动词来帮忙,
(完整word版)高中英语动词时态语态复习讲解
高中英语时态语态讲解 1、一般现在时主要用来表示人、事物的现在状况和特点;表示经常或习惯性的动作;表示客观规律和永恒真理;按照计划安排好了将要发生的动作(一般指时 刻表)等 He usually goes to w ork at 7 o’clock every morning. The train to Shanghai leaves at 7am. 考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。如:I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 考点二:在时间、方式、让步和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, once, the moment/the minute, the day; 条件:if, unless, provided. If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon. 只要他努力工作,我不介意他什么时候做完试验。 2、现在进行时 表说话时或目前一段时间内正在进行的活动;或表感情色彩,加强语气。与频率副词,如always,constantly,continually,again等连用表示说话人的某种感情色彩(赞叹、厌烦、埋怨等)。 We are having English class. The house is being built these days. The little boy is always making trouble. 考点一:在时间状语或条件状语从句中表示将来正在进行的动作。Look out when you are crossing the street. Don't wake him up if he is still sleeping at 7 tomorrow morning. 考点二:表示在最近按计划或安排要进行的动作(这时多有表示将来的时间状语)。 Marry is leaving on Friday. 3、现在完成时 (1)非延续动作:动作发生在过去,对现在有影响。(2)延续性动作:动作和状态的持续。现在完成时有一些标志性的时间状语: 考点一:for + 时间段;since + 时间点 They have lived in Beijing for five years. They have lived in Beijing since 1995. 考点二:常见的不确定的时间状语:lately; recently, just, already, yet, up to now; till now; so far, these days, Has it stopped raining yet ? 考点三:在表示“最近几世纪/ 年/ 月以来……”时间状语中,谓语动词用现在完成时。 in the past;over the past; during the last等 考点四:表示“第几次做某事,”或在“It is the best (worst, most interesting ) +名词+that” 后面,主句是一般现在时态时,从句用现在完成时。 This is my first time that I have visited China. This is the most interesting film I have ever seen. 4.一般过去时 表在过去某个特定时间发生且完成的动作,或过去习惯性动作,不强调对现在的影响,只说明过去。常跟明确的过去时间连用, 注意: 考点一:used to + do,表示过去经常但现在已不再维持的习惯动作。 be/become/get used to + doing,表示习惯于 He used to smoke a lot. He has got used to getting up early. 考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替过去将来时。 He promised to buy me a computer if he got a raise 5. 过去进行时
初中英语语法专项复习——英语动词时态和语态讲解和练习题教学文案
初中英语语法专项复习:英语各个时态和语态讲解及练习题 初中英语有16种时态,但是常用的只有9种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。下面分别介绍。 1、一般现在时的用法 (1)一般现在时表示经常性、习惯性的动作;表示现在的状态、特征和真理。句中常用 always,usually,often,sometimes,seldom,rarely,never, every day(morning,Monday,week,...etc.) ,every there years, once a week(day,month,...etc.),...等时间状语。例如: a. He goes to school every day. b. He is very happy. c.The earth moves around the sun. 2) 在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来。例如: a. If you come this afternoon, we’ll have a meeting. b. When I graduate, I’ll go to countryside. 2.一般过去时的用法 (1)表示过去某时间发生的事、存在的状态或过反复发生的动作。常和: last week(night,Monday,month,year,...etc.) four years ago(days,month,...etc.) before1980(three,liberation,从句,...etc.) the day before yesterday,the day before last, the year before last,just now,a monent ago, yesterday,yesterday morning,this morning, at first,at last,in the end,finally,then,.. a. He saw Mr. Wang yesterday. b. He worked in a factory in 1986. 2)表示过去经常发生的动作,也可用“used to “ 和“would + 动词原形”。I used to smoke. During the vacation I wouldm in the sea. 注:”used to “ 表示过去常发生而现在不再发生的动作或存在的状态。 a. I am used to the climate here. b. He is used tomming in winter. 3.一般将来时的用法 一般将来时表示将来的动作或状态。其表达形式除了“ will 或shall + 动词原形”表示即将发生的或最近打算进行的事。常和:next week(Monday,month,year,...etc.) in three days(an hour,...etc.) tomorrow,tomorrow morning,the day after tomorrow,the day after next,the year after next,tonight,in 2010(2016...etc.) this evening,this Saturday,after Wednesday,soon,sometime next week,one day in futuer,sooner or later,... 1)be going to do 结构 It is going to rain. We are going to have a meeting today. 2) “be about to + 动词原形” 表示即将发生的动作,意为be ready to do sth. 后面一般不跟时间状语。We are about to leave. 3) go , come , start, move, leave, arrive ,stay 等可用进行时态表示按计划即将发生的动作。I’m leaving for Beijing. 4.现在进行时的用法 1)现在进行时表示现在正在进行的动作,由“ be + 现在分词” 构成。常和:now,these days(weeks,months,...etc.) this month(week,...etc.) Look!,Listen!,... 另外,“系动词+ 介词或副词” 也表示进行时的意义。What are you doing? The bridge is under construction. 2)表示感觉、愿望和状态的某些动词(如have, be , here, se, like 等)一般不用进行。 5.过去进行时的用法 1)过去进行时过去某一时刻、某一阶段正进行的动作,由“ was (were) + 现在分词”构成。 常和:this time yesterday,this time last Friday,in those days,at nine last night,from one to three yesterday afternoon,... In 1980 he was studying in a university. He was reading a novel when I came in.
高中英语动词的时态和语态讲解
动词的时态和语态用法详解 在英语中,不同时间里发生的动作或存在的状态需要用动词的不同形式表示出来,动词的这种不同 形式就构成了动词的时态。 英语中的时态按动作发生时间分为现在时态、过去时态、将来时态 二、常见时态的基本用法 1. 一般现在时:一般现在时是描述现在或经常性的动作性质或状态的时态。常和表示频率、时间的副词 (短语) always, every time, now and the n, occasi on ally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually 连用。 1) 表示经常性或习惯性的动作。 We have three meals a day. 2) 表示客观事实、真理和自然现象。 Kno wledge is power. 3)表示现在的情况或状态。 I live in Beiji ng. 4)表示已经“列入日程”的将来的事件,尤其指计划中的和安排好的将来的动作,这些动词往往表示“出 发,到达”等含义 的词, 女口, arrive, begin, go, leave, start, stay 等。 The train arrives at 10:30. There's ple nty of time. 。 考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。 如: I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, on ce, the mome nt/the minu te, the day; 条件:if, uni ess, provided. If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon. 考点三:在 make sure (certain), see to it, mind, care, matter 替一般将来时。 So long as he works hard, I don ' t mind when he finish 考点四:在 the more …the more …(越 ..................... 越 ... )句型中 在时。 The harder you study, the better results you will get. 2. 一般过去时:一般过去时表示过去发生的动作、存在的状态,或反复发生的动作,句中一般都有表示 过去具体时间的时间 状语。 1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或状态。 此时与表示过去的时间状语连用, 如yesterday, last week, an hour ago, the other day, in 1998 等。 +宾语从句,从句用一般现在时代 es the experime nt. ,若主句是一般将来时,从句通常用一般现
英语时态8种基本时态讲解[1]演示教学
英语时态8种基本时态讲解[1]
英语时态8种基本时态讲解 一.概念:英语中表示不同时间发生的动作或存在的状态,需用不同的动词形式表示,这种不同的动词形式称为时态。 二.种类:(基本时态) 一般现在时一般过去时 现在进行时过去进行时 一般将来时过去将来时 现在完成时过去完成时 三.用法: 1)一般现在时表示经常发生或习惯性的动作或状态及客观现实和普遍真理。 一般现在时常以动词原形表示,但当主语是第三人称单数时,动词词尾加-s或-es。 2)句型结构:主语+V.(包括be动词)+宾语+… She is an engineer. He has breakfast at 6:00 every day. 3)注意: a)一般现在时通常与always , often , usually , every day , sometimes , once a week 等时间状语连用。 I always watch TV at 8:00 in the evening. They go home once a week. We usually do our homework at home.
b)表客观现实或普遍真理。 The sun always rises in the east. The light travels faster than the sound. c)表永远性的动作或状态。 He lives in the country. 4)第三人称单数变化形式。 a)一般情况动词在词尾加-s . come---comes speak---speaks work---works live---lives b)以o, s, x, ch, sh结尾的单词在词后加-es. do---does go---goes finish---finishes brush---brushes fix---fixes pass---passes watch---watches c)以“辅音字母+y”结尾的单词变y为i加-es. Study---studies carry-carries cry---cries d)以“元音字母+y”结尾的单词直接加-s. play---plays stay---stays 例句:我们每天晚上九点做作业。 我在早上七点半起床。 他每天七点去上班。 我们经常下午打篮球。 他喜欢音乐。 地球围绕太阳转。
高中16种英语时态总结归纳
时态(Tense)是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时。 1. 一般现在时 用法: A) 表示现在发生的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯用语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别人。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。尤其要注意,如果前后文不是一般现在时,则无法保持主句、从句时态一致。 E) 表示一个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作,(仅限于某些表示“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表示未来时间的状语搭配使用。常见的用法是:飞机、火车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运行的交通方式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下一趟火车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久一趟?) F) 在时间和条件状语从句里经常用一般现在(有时也用现在完成时)表示将来事情。 例:When you have finished the report, I will have waited for about 3 hours.(等你完成这份报告的时候,我就已经等了将近3个小时了。) 2. 现在进行时(be doing) 用法:现在正在进行的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) 用法: A) 表示动作到现在为止已经完成或刚刚完成。 例:I bought a new house, but I _________ my old one yet, so at the moment I have two houses. A) didn't sell B) sold C) haven't sold D) would sell 答案是C) haven't sold。 B) 表示从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常用延续性动词。时间状语常用since加一个过去的时间点,或for加一段时间,或by加一个现在时间。 例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modified by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged B) may be challenged D) are challenging
英语时态8种基本时态讲解教学文案
英语时态8种基本时 态讲解
英语时态8种基本时态讲解 一.概念:英语中表示不同时间发生的动作或存在的状态,需用不同的动词形式表示,这种不同的动词形式称为时态。 二.种类:(基本时态) 一般现在时一般过去时 现在进行时过去进行时 一般将来时过去将来时 现在完成时过去完成时 三.用法: 1.一般现在时: 1)一般现在时表示经常发生或习惯性的动作或状态及客观现实和普遍真理。 一般现在时常以动词原形表示,但当主语是第三人称单数时,动词词尾加-s或-es。 2)句型结构:主语+V.(包括be动词)+宾语+… She is an engineer.
He has breakfast at 6:00every day. 3)注意: a)一般现在时通常与always , often , usually , every day , sometimes , once a week 等时间状语连用。 I always watch TV at 8:00 in the evening . They go home once a week . We usually do our homework at home . b)表客观现实或普遍真理。 The sun always rises in the east . The light travels faster than the sound . c)表永远性的动作或状态。 He lives in the country .
4)第三人称单数变化形式。 a)一般情况动词在词尾加-s . come---comes speak---speaks work---works live---lives b)以o, s, x, ch, sh结尾的单词在词后加-es. do---does go---goes finish---finishes brush---brushes fix---fixes pass---passes watch---watches c)以“辅音字母+y”结尾的单词变y为i加-es. Study---studies carry-carries cry---cries d)以“元音字母+y”结尾的单词直接加-s. play---plays stay---stays 例句:我们每天晚上九点做作业。 我在早上七点半起床。
高中英语时态分析教学
高中英语时态分析教学 随着新课程改革的深入推进,学生在学习中主体地位的突现,教师作为课堂教学的主导者在进行教学时重过程,重导其表而疏其实。而学生在进行语法学习时,鉴于教师的过程化教学,往往容易形成对于知识的理解、掌握流于表象,对其实质知之甚少,让其说出各种时态的差异及用法时,绝大多数学生能迅速、流利“背”出相关理论性语言,但在具体运用时则不知所以然,甚至张冠李戴,导致错误。笔者从07年新课程改革全面实施以来,一直认真研读高中语法在新教材中的编排理论,及高中教师如何对新教材下语法知识的传导。结合自己在日常教学中的实践摸索,我认为高中英语时态教学中应从以下几个方面培养学生分析时态。 一、从概念入手 时态的概念是时态的本质。各种时态的概念诠释了各种时态谓语动词动作发生的内在实质,这是英语语言与作为我们母语的汉语所没有的特点。我们在教学中有对时态概念的分析,但流于表象、较抽象,学生难于从其实质上理解。部分学生仅仅从一般概念意义上去背诵、记忆,而无法从概念实质上去分析具体时态。怎么正确运用时态的概念去解决具体问题呢? 首先应了解时态概念的实质。时态概念界定了谓语动词动作发生的时间范畴;谓语动词动作发生后,该动作所产生的影响;以及该动词动作本身具有的特征。如: 1、一般现在时:概念是经常性、习惯性的动作。 例:I usually get up at six in the morning. 时间范畴:任意一天的早晨 动作产生的影响:早6:00点起床。 动作的特征:动作在过去、现在、将来都会发生。 2、一般过去时:强调动作发生在过去的一个事实。 例:He went to Beijing last week. 时间范畴:过去特定的一个时间(last week) 动作影响:上周去了北京,至于现在情况则不清楚。 动作特征:上周(last week)该动作发生过,与现在无关。 3、现在完成时:动作发生在过去,但过去的时间不清楚,对现在造成一定的影响或结果。 例:I have read the book three times. 时间范畴:动作发生在一个不太清楚的过去。 动作影响:对现在又一定的影响,即主语对book有一定的了解。 动作特征:过去的动作与现在有关。 4、过去进行时:动作发生在过去特定的时间,强调过去动作的持续,与现在没有关系。 例:---can you tell me what I said just now? ---Sorry ,I was observing the dog near the river.
高中英语动词时态语态讲解及练习
1、一般现在时主要用来表示人、事物的现在状况和特点;表示经常或习惯性的动作,句子中常有often, always, from time to time 等时间状语;表示客观规律和永恒真理等。He usually goes to w ork at 7 o’clock every morning. The earth goes around the sun. Guangzhou is situated in the south of China. 考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。如:I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school. 考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, once, the moment/the minute, the day; 条件:if, unless, provided. If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon. 考点三:在make sure (certain), see to it, mind, care, matter +宾语从句,从句用一般现在时代替一般将来时。 So long as he works hard, I don’t mind when he finishes the experiment. 只要他努力工作,我不介意他什么时候做完试验。 考点四:在the more… the more … (越……越……) 句型中, 若主句是一般将来时, 从句通常用一般现在时。 The harder you study, the better results you will get. 2、现在进行时 表说话时或目前一段时间内正在进行的活动:或表感情色彩,加强语气。与频率副词,如always,constantly,continually,again等连用表示说话人的某种感情色彩(赞叹、厌烦、埋怨等)。
高中16种英语时态总结归纳PDF
时态 时态(Tense)是表??为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。 1. ?般现在时 ?法: A) 表?现在发?的动作、情况、状态和特征。 B) 习惯?语。 C) 经常性、习惯性动作。 例:He always helps others. (他总是帮助别?。) D) 客观事实和普遍真理。 E) 表??个按规定、计划或安排要发?的动作,(仅限于某些表?“来、去、动、停、开始、结束、继续”等的动词)可以与表?未来时间的状语搭配使?。常见的?法是:飞机、?车、轮船、汽车等定期定点运?的交通?式。 例:The next train leaves at 3 o'clock this afternoon. (下?趟?车今天下午3点开车。) How often does this shuttle bus run? (这班车多久?趟?) 2. 现在进?时(be doing) ?法:现在正在进?的动作。 3. 现在完成时(have done) ?法: A) 表?动作到现在为?已经完成或刚刚完成。 B)表?从过去某时刻开始,持续到现在的动作或情况,并且有可能会继续延续下去。此时经常?延续性动词。时间状语常?since加?个过去的时间点,或for加?段时间,或by加?个现在时间。 例:Great as Newton was, many of his ideas ___________ today and are being modi?ed by the work of scientists of our time. A) are to challenge C) have been challenged B) may be challenged D) are challenging C) 表?发?在过去,但对现在仍有影响的动作或情况。通常?点动词,如:arrive, begin, ?nd, give, lose等。例:John has broken his left leg.(约翰摔断了左腿。) 【注意事项】 A)现在完成时是联系过去和现在的纽带。现在完成时和过去时的区别在于:现在完成时强调动作的动态,或受动态的影响,是动态的结果,对现在有影响;过去时只表?过去的某个具体时间?发?的动作,与现在没有联系。 例:He worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他曾经在那家医院?作了8年。这只是讲述?个过去的事实,他现在已经不在那家医院了。) He has worked in that hospital for 8 years.(他已经在那家医院??作了8年。表?他从过去开始?作,?直?作到现在,现在仍在那家医院?作。) B)因为含有for加?段时间或since加?个时间点这样的时间状语的完成时,有动态和延续性的特点,所以不能使?终端动词或瞬间动词。 例:My sister has been married for 5 years.(过去分词做表语表?状态,可以延续) My sister has married. Don't disturb her.(终端动词) C) 在"this is the ?rst/ second/ third…… time that……"句型?要求?完成时。 例:This is the second time that the products of our company have been shown in the International Exhibition.(这是我公司产品第?次参加国际展览会。) D) 句型"It is/ has been……since"所使?的两种时态都正确。 例:It is/ has been 10 years since I last saw him.(从我上次见到他以来已经10年了。)
高考英语动词的时态和语态讲解
v1.0 可编辑可修改 时态语态 (一)时态 一般现在时表示:1.现在的经常性、习惯性动作 eg: I read English every morning. 2.客观真理、普遍公立、科学事实eg: The sun rises in the east. 3.现有的兴趣、爱好或能力eg: He likes playing football. 4.现存的性质、特征或状态eg: The situation is encouraging. 5.介绍故事剧情、新闻标题eg: Workers face tough times abroad. 6.按时刻表或按规定计划、安排将要放生的动作(常见动词如:come, go, leave, arrive, begin, start, takeoff, return, stop, open, close等)eg: The train leaves at 4:30 . 注意:here, there, now, then 等开头的倒装句要用一般现在时代替现在进行时。如: Look! Here comes the bus. 一般过去时表示:1.过去经常性、习惯性的动作或状态eg: He often cried when he was a boy. 2.过去某时的状态或动作 eg: I went to the bank just now. 3.用于 I didn’t know…或 I forgot…,表示实现不知道或不记得,但现在已经知道或记得的事情。eg: I didn’t know you were here. Sorry, I forgot to bring my book. 注意:表示过去经常发生的动作,也可以用“used to do…”和“ would do” 一般将来时表示:1.现在看来以后要发生的动作或存在的状态eg: Tom will come next week. 2.事物的固有属性或必然趋势eg: Oil will float in water. Fish will die without water. 3.对将来某个动作的安排、计划eg: He is going to speak on TV this evening. 注意:将来时常见表达形式:will/ shall do; be going to do; be to do; be about to do (此形式不能与时间状语连用) 现在进行时表示:1.此时此刻正在发生的动作eg: I’m studying English now. 2.现阶段正在发生的动作eg: We are building our socialism. 3.情况的暂时性eg: I don’t really work here. I am just helping until the secretary arrives. 4.与 always, forever, constantly, continually 连用,表示参上或厌恶等感情色彩,但并非强调动作正在进行eg: He is always helping others. She is always forgetting something. 5.按计划、安排近期发生的动作(只限于come, go, leave, arrive, start, move, sail, fly, travel, stay等动词)eg: A foreigner is coming to visit our school. I’m leaving for Beijing tomorrow. 注意:不宜用进行时的动作:感觉类: look, smell, feel, sound, taste, see, hear 情感类:like, love, prefer, admire, hate, fear 心态类:wish, hope, expect, want, need, believe, thin, understand, agree, know, remember, forget 所有类:have, contain, won, hold, belong to 过去进行时表示:1.过去某一时刻或阶段发生的动作eg: He was watching TV this time yesterday. 2.与 always, forever, constantly, continually 连用,表示赞赏或亚无等感情色彩eg: Comrade Lei Feng was always thinking of others never thinking of himself. 3.过去计划、安排好的将来动作(只限于 come, go, leave, arrive, start, move, sail, fly, travel, stay 等动词)eg: He said he was leaving the next day. I was told the train was starting soon. 注意:过去进行时可用来描绘故事发生的背景,如:The wind was blowing and it was raining hard. 过去将来时表示:1.过去某一时刻后将要发生的过去动作或过去的意图、打算(主要用于宾语从句中)eg: She was sure she would succeed. I thought you would come. 注意:把一般将来时中的助动词变成过去式,便成了过去将来时的表达形式 现在完成时表示:1.现在已完成或刚刚完成且对现在有影响的动作eg: I have finished my homework. 2.表示始于过去持续至今的动作或状态eg: He’s lived here since 2005. I’ve taught
英语8种时态教学内容
英语8种时态
初中英语八种时态归纳复习 时态是英语学习中一个至关重要的内容,广大初中学生在实际运用时,往往对时态问题倍感棘手,下面我们就归纳复习一下这几种时态。 一、一般现在时 (一)定义 表示经常性或习惯性的动作,或存在的状态,还表示主语具备的性格和能力及客观真理。 例:I get up at 6:30 in the morning . She is at home . (二)构成 主要用动词原形表示,当主语是第三人称单数时,在动词词尾加s/es。 (三)句型 1、肯定句:主语+谓语+其他。 She reads English everyday . 2、否定句:主语+don’t/doesn’t+谓语+其他。 He doesn’t get up at 6:30 in the morning . 3、一般疑问句:Do/Does+主语+V原+其他? Do you like English ? Yes ,I do ./No, I don’t . 4、特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+do/does+主语+V原+其他? What time do you get up every morning ? Where does your father work ? (三)用法 1、表示经常性或习惯性的动作,或存在的状态,带与表示频率的时间状语如:often , sometimes , usually,always , everyday year, month...) , once/twice a week (month , year , etc.) , seldom , on Sundays等连用。 I leave home for school at seven every morning .
