所有者权益(或股东权益)增减变动表~中英文对照
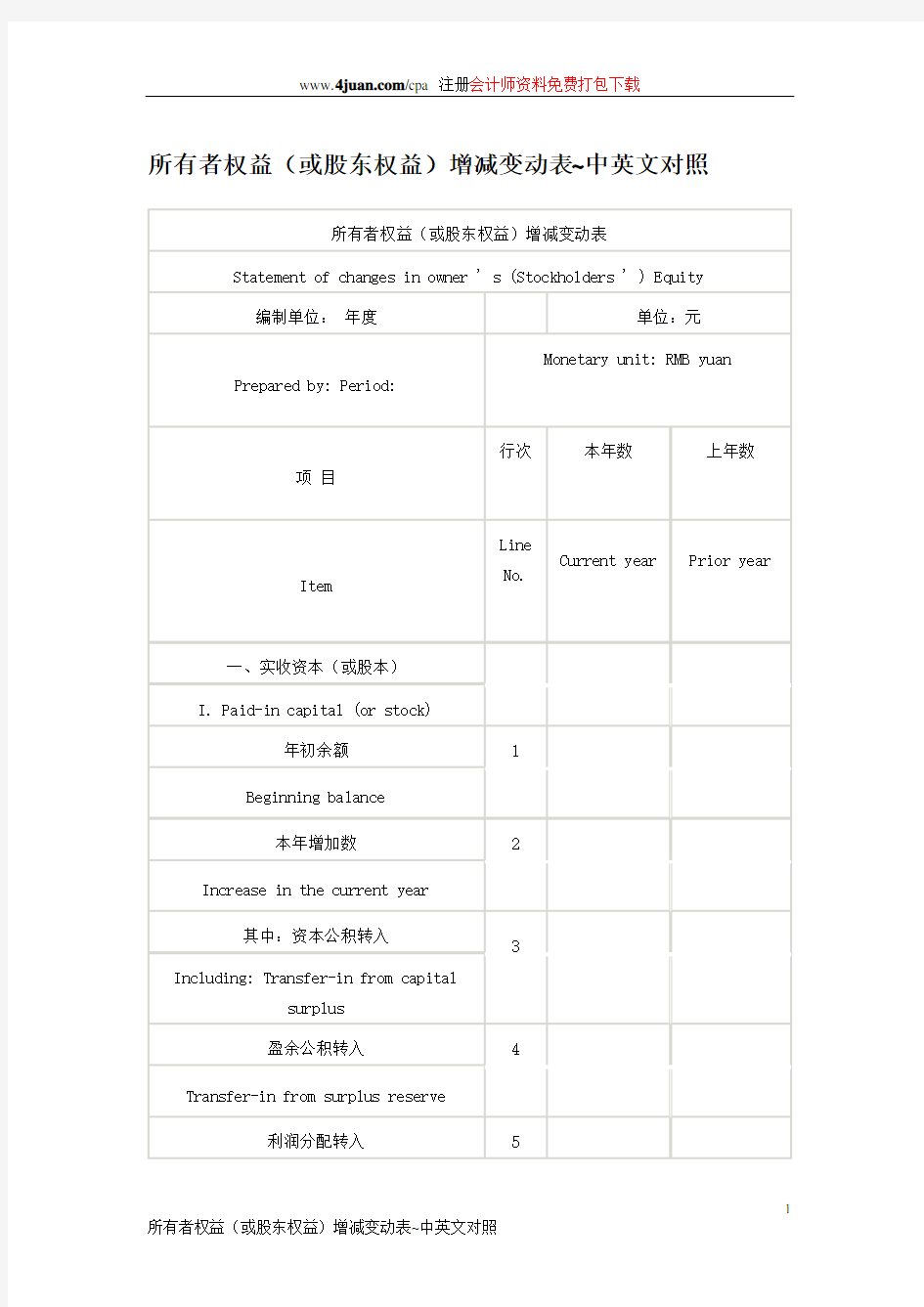
所有者权益(或股东权益)增减变动表~中英文对照
第5章 所有者权益变动表分析习题答案
第五章所有者权益变动分析 一.单项选择题 1.B 2.D 3.C 4.A 5.B 6.D 7.A 二.多项选择题 1.BC 2.ABC 3.CDE 4.ABDE 5.ABCDE 6.ABCDE 7.ABCE 8.ABCD 三.判断题 1.错误。所有者权益变动表可以反映投资人或者股东所拥有的权益,据以判断资本保 值,增值的情况以及对负债的保障程度。 2.错误。所有者权益净变动额等于资产负债表中的期末与期初所有者权益的差额。 3.正确。 4.正确。 5.错误。库存股可以再次出售。 6.正确。 7.错误。转增股本是指公司将资本公积转化为股本,它并没有改变股东的权益规模。 8.错误。股票股利会影响所有者权益内部的结构,而股票分割则不会改变公司的所有 者权益结构。 9.正确。 10.正确。 四.简答题 1.简述所有者权益变动表与其他会计表报的关系。 资产负债表报告的是某一时点的价值存量,利润表,现金流量表与所有者权益变动表反映的是两个时点之间的存量变化—流量,利润表反映了所有者权益变化的一部分,现金流量表则反映了现金的变化过程,所有者权益变动表反映的是资产负债表中所有者权益具体项目的变化过程。四张会计表用会计语言反映了会计期间的总体财务状况和经营业绩。 2.如何理解《企业会计准则---基本准则》中的所有者权益要素? 所有者权益是指企业资产扣除负债后由股东享有的“剩余价值”,也称为净资产,是股东投资资本与经营过程中形成的留存收益的集合,是股东投资和公司发展实力的资本体现。 3.如何进行所有者权益变动表的水平分析? 所有者权益变动表的水平分析,是指所有者权益各个项目的本期数与基准(可以是上期数等)进行对比,揭示公司当期所有者权益各个项目的水平及其变动情况,解释公司净资产的变动原因,借以进行相关决策的过程。 4.简述所有者权益变动的原因 所有者权益变动的原因可简单归纳为以下几点: 1.本期净利润 2.直接计入所有者权益的利得与损失 3.会计政策和会计差错更正的累积影响 4.股东投入资本 5.向股东分配利润 6.提取盈余公积
所有者权益变动表格式及其内容填写
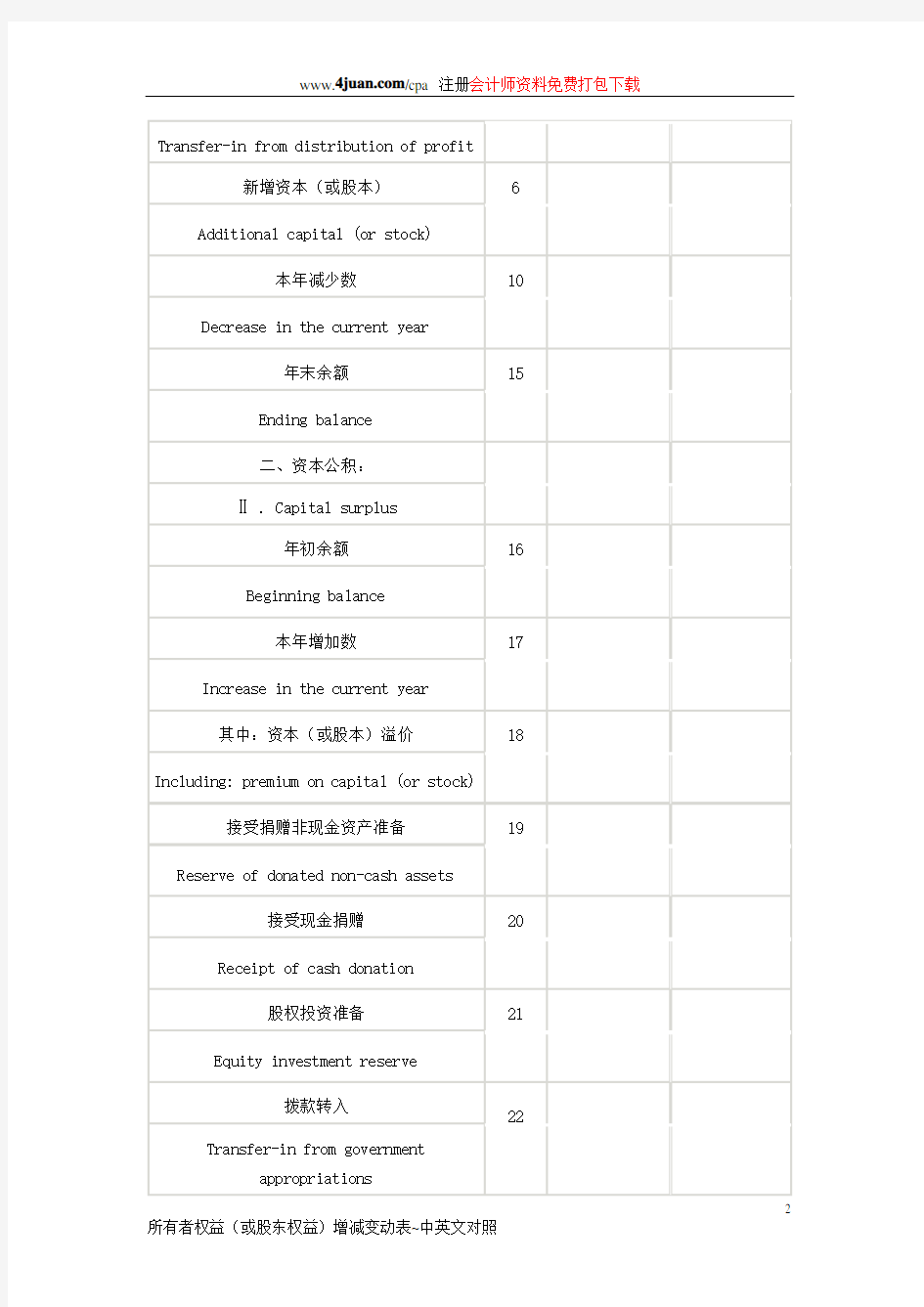
般企业所有者权益变动表的列报方法 1.所有者权益变动表各项目的列报说明 (1)“上年年末余额”项目,反映企业上年资产负债表中实收资本(或股本)、资本公积、盈余公积、未分配利润的年末余额。 (2)“会计政策变更”和“前期差错更正”项目,分别反映企业采用追溯调整法处理的会计政策变更的累积影响金额和采用追溯重述法处理的会计差错更正的累积影响金额。为了体现会计政策变更和前期差错更正的影响,企业应当在上期期末所有者权益余额的基础上进行调整得出本期期初所有者权益,根据“盈余公积”、“利润分配”、“以前年度损益调整”等科目的发生额分析填列。 (3)“本年增减变动额”项目分别反映如下内容: ①“净利润”项目,反映企业当年实现的净利润(或净亏损)金额, 并对应列在“未分配利润”栏。 ②“其他综合收益”项目,反映企业当年根据企业会计准则规定未在 损益中确认的各项利得和损失扣除所得税影响后的净额,并对应列在“资本公积”栏。 ③“净利润”和“其他综合收益”小计项目,反映企业当年实现的净 利润(或净亏损)金额和当年计入其他综合收益金额的合计额。 ④”所有者投入和减少资本”项目,反映企业当年所有者投入的资本和减少的资本其中:“所有者投入资本”项目,反映企业接受投资者投入形成的实收资本(或股本)和资本溢价或股本溢价,并对应列在”实收资本”和”资本公积”栏。“股份支付计入所有者权益的金额”项目,反映企业处于等待期中的权益结算的股份支付当年计入资本公积的金额,并对应列在”资本公积”栏。 ⑤“利润分配”下各项目,反映当年对所有者(或股东)分配的利润(或股利)金额和按照规定提取的盈余公积金额,并对应列在“未分配利润”和“盈余公积”栏。其中: “提取盈余公积”项目,反映企业按照规定提取的盈余公积。 “对所有者(或股东)的分配”项目,反映对所有者(或股东)分配的利润(或股利)金额。 ⑥“所有者权益内部结转”下各项目,反映不影响当年所有者权益总 额的所有者权益各组成部分之间当年的增减变动,包括资本公积转增资本(或股本)、盈余公积转增资本(或股本)、盈余公积弥补亏损等项金额。为了全面反映所有者权益各组成部分的增减变动情况,所有者权益内部结转也是所有者权益变动表的重要组成部分,主要指不影响所有者权益总额、所有者权益的各组成部分当期的增减变动。其中:
资产负债表水平分析
资产负债表水平分析 一、资产负债表水平分析表的编制 将分析期的资产负债表各项目数值与基期(上年或计划、预算)数进行比较,计算出变动额、变动率以及该项目对资产总额、负债总额和所有者权益总额的影响程度。 二、资产负债表变动情况的分析评价 (一)从投资或资产角度进行分析评价 1、分析总资产规模的变动状况以及各类、各项资产的变动状况; 2、发现变动幅度较大或对总资产影响较大的重点类别和重点项目; 3、分析资产变动的合理性与效率性; 4、考察资产规模变动与所有者权益总额变动的适应程度,进而评价企业财务结构的稳定性和安全性; 5、分析会计政策变动的影响。(二)从筹资或权益角度进行分析评价 1、分析权益总额的变动状况以及各类、各项筹资的变动状况; 2、发现变动幅度较大或对权益影响较大的重点类别和重点项目; 3、注意分析评价表外业务的影响。(三)资产负债表变动原因的分析评价 1、负债变动型 2、追加投资变动型 3、经营变动型 4、股利分配变动型。 资产负债表垂直分析 一、资产负债表垂直分析表的编制 通过计算资产负债表中各项目占总资产或权益总额的比重,分析评价企业资产结构和权益结构变动的合理程度。 静态分析:以本期资产负债表为对象动态分析:将本期资产负债表与选定的标准进行比较。 二、资产负债表结构变动情况的分析评价 (一)资产结构的分析评价 1、从静态角度观察企业资产的配置情况,通过与行业平均水平或可比企业的资产结构比较,评价其合理性; 2、从动态角度分析资产结构的变动情况,对资产的稳定性做出评价。(二)资本结构的分析评价 1、从静态角度观察资本的构成,结合企业盈利能力和经营风险,评价其合理性; 2、从动态角度分析资本结构的变动情况,分析其对股东收益产生的影响。 三、资产结构、负债结构、股东权益结构的具体分析评价 (一)资产结构的具体分析评价 1、经营资产与非经营资产的比例关系 2、固定资产和流动资产的比例关系:适中型、保守型、激进型。 3、流动资产的内部结构与同行业平均水平或财务计划确定的目标为标准(二)负债结构的具体分析评价 1、负债结构分析应考虑的因素(1)负债结构与负债规模(2)负债结构与负债成本(3)负债结构与债务偿还期限(4)负债结构与财务风险(5)负债结构与经济环境(6)负债
会计英语-单词表 谷丰
专业词汇汇总表 Chapter 1 Non-for-profits organization 非赢利组织Service 服务 Manufacture生产 Merchandise 商品 Accounting会计 Management管理层 Accounting system记帐系统 Financial accounting财务会计Financial report财务报告 Decision-making决策制定 Audit 审计 Management accounting管理会计Cost accounting成本会计 Operating cost 生产费用,营业成本Budgeting预算 Accumulate累积 Accounting process核算过程Transaction交易,业务 Events事项 Expenses费用
Income收入 Identify确认 Measure计量 Record记录 Communicate沟通 Financial position财务状况Performance经营 Entity实体 Enterprise企业 Balance sheet 资产负债表 Statement of financial position财务状况表Equity权益 Debt债务 Return回报 Creditors债权人 Supplier供应商 Customer客户 Economic resource经济资源 Financial structure财务结构 Liquidity流动性 Solvency偿债能力 Cash现金
Cash equivalents现金等价物 Financial performance 财务业绩 Accrual basis权责发生制 Assets资产 Liabilities负债 Equity权益 Going concern永续经营 Liquidate清算,清盘(破产公司) Economic entity经济实体 Unit of measurement货币计量 Accounting period会计分期 GAAP (general accepted accounting principle)一般公认会计准则 Profitability获利能力 China Securities Regulatory Commission(CSRC) 中国证监会Listed company上市公司 Disclose披露 Understandability可理解性 Relevance相关性 Reliability可靠性 Comparability可比性
财务会计报最新表中英文对照
?会计报表中英文对照
Accounting 1. Financial reporting(财务报告) includes not only financial statements but also other means of communicating information that relates, directly or indirectly, to the information provided by a business enterprise’s accounting system----that is, information about an enterprise’s resources, obligations, earnings, etc. 2. Objectives of financial reporting: 财务报告的目标 Financial reporting should: (1) Provide information that helps in making investment and credit decisions. (2) Provide information that enables assessing future cash flows. (3) Provide information that enables users to learn about economic resources, claims against those resources, and changes in them. 3. Basic accounting assumptions 基本会计假设 (1) Economic entity assumption 会计主体假设 This assumption simply says that the business and the owner of the business are two separate legal and economic entities. Each entity should account and report its own financial activities. (2) Going concern assumption 持续经营假设 This assumption states that the enterprise will continue in operation long enough to carry out its existing objectives. This assumption enables accountants to make estimates about asset lives and how transactions might be amortized over time. This assumption enables an accountant to use accrual accounting which records accrual and deferral entries as of each balance sheet date. (3) Time period assumption 会计分期假设 This assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods. The most typical time segment = Calendar Year Next most typical time segment = Fiscal Year (4) Monetary unit assumption 货币计量假设 This assumption states that only transaction data that can be expressed in terms of money be included in the accounting records, and the unit of measure remains relatively constant over time in terms of purchasing power. In essence, this assumption disregards the effects of inflation or deflation in the economy in which the entity operates. This assumption provides support for the "Historical Cost" principle. 4. Accrual-basis accounting 权责发生制会计 5. Qualitative characteristics 会计信息质量特征 (1) Reliability 可靠性 For accounting information to be reliable, it must be dependable and trustworthy. Accounting information is reliable to the extend that it is: Verifiable: means that information has been objectively determined, arrived at, or created. More than one person could consider the facts of a situation and reach a similar conclusion. Representationally faithful: that something is what it is represented to be. For example, if a machine is listed as a fixed asset on the balance sheet, then the company can prove that the machine exists, is owned by the company, is in working condition, and is currently being used to support the revenue generating activities of the
股东权益(所有者权益)增减变动表编制说明
股东权益(所有者权益,下同)增减变动表,是反映企业在某一特定日期股东权益增减变动情况的报表。股东权益增减变动表包括在年度会计报表中,是资产负债表的附表。 股东权益增减变动表全面反映了企业的股东权益在年度内的变化情况,便于会计信息使用者深入分析企业股东权益的增减变化情况,并进而对企业的资本保值增值情况作出正确判断,从而提供对决策有用的信息。 股东权益增减变动表包括表首、正表两部分。其中,表首说明报表名称、编制单位、编制日期、报表编号、货币名称、计量单位等;正表是股东权益增减变动表的主体,具体说明股东权益增减变动表的各项内容,包括股本(实收资本)、资本公积、法定和任意盈余公积、法定公益金、未分配利润等。每个项目中,又分为年初余额、本年增加数、本年减少数、年末余额四小项,每个小项中,又分别具体情况列示其不同内容。 股东权益增减变动表各项目应根据“股本”、“资本公积”、“盈余公积”、“未分配利润”等科目的发生额分析填列。
三、但愿有一天你会记起,我曾默默地,毫无希望地爱过你。我这扇门曾为你打开,只为你一人打开,现在,我要把它关上了。 四、你看我的时候我装做在看别处,你在看别处的时候我在看你。 五、陆上的人喜欢寻根究底,虚度很多的光阴。冬天担忧夏天的迟来,夏天担心冬天的将至。所以你们不停到处去追求一个遥不可及,四季如夏的地方,我并不羡慕。 六、没想到的是,一别竟是一辈子了。 七、朋友们都羡慕我,其实羡慕他们的人是我。爱你,很久了,等你,也很久了,现在,我要离开你了,比很久很久还要久…… 八、Do something today that your future self will thank you for. 从现在开始,做一些让未来的你感谢现在的自己的事。 九、有个懂你的人,是最大的幸福。这个人,不一定十全十美,但他能读懂你,能走进你的心灵深处,能看懂你心里的一切。最懂你的人,总是会一直的在你身边,默默守护你,不让你受一点点的委屈。真正爱你的人不会说许多爱你的话,却会做许多爱你的事。 十、很久很久,没有对方的消息,也不再想起这个人,也是不想再想起。 十一、我不怕我会忘记他,他在我心底开出了花。 十二、我还在原地等你,你却已经忘记曾来过这里。 十三、那都是很好很好的,我却偏偏不喜欢。 十四、向来缘浅,奈何情深? 十五、习惯难受,习惯思念,习惯等你,可是却一直没有习惯看不到你 十六、爱一个人最好的方式,是经营好自己,给对方一个优质的爱人。不是拼命对一个人好,那人就会拼命爱你。俗世的感情难免有现实的一面:你有价值,你的付出才有人重视。——苏芩
财务报表各项目中英文对照
财务报表各项目中英文对照 一、损益表INCOME STATEMENT Aggregate income statement 合并损益表 Operating Results 经营业绩 FINANCIAL HIGHLIGHTS 财务摘要 Gross revenues 总收入/毛收入 Net revenues 销售收入/净收入 Sales 销售额 Turnover 营业额 Cost of revenues 销售成本 Gross profit 毛利润 Gross margin 毛利率 Other income and gain 其他收入及利得 EBITDA 息、税、折旧、摊销前利润(EBITDA) EBITDA margin EBITDA率 EBITA 息、税、摊销前利润 EBIT 息税前利润/营业利润 Operating income(loss)营业利润/(亏损) Operating profit 营业利润 Operating margin 营业利润率 EBIT margin EBIT率(营业利润率) Profit before disposal of investments 出售投资前利润 Operating expenses: 营业费用: Research and development costs (R&D)研发费用 marketing expenses Selling expenses 销售费用 Cost of revenues 营业成本 Selling Cost 销售成本 Sales and marketing expenses Selling and marketing expenses 销售费用、或销售及市场推广费用 Selling and distribution costs 营销费用/行销费用 General and administrative expenses 管理费用/一般及管理费用 Administrative expenses 管理费用 Operating income(loss)营业利润/(亏损) Profit from operating activities 营业利润/经营活动之利润 Finance costs 财务费用/财务成本 Financial result 财务费用 Finance income 财务收益 Change in fair value of derivative liability associated with Series B convertible redeemable preference shares 可转换可赎回优先股B相关衍生负债公允值变动 Loss on the derivative component of convertible bonds 可換股債券衍生工具之損失 Equity loss of affiliates 子公司权益损失 Government grant income 政府补助 Other (expense) / income 其他收入/(费用)
所有者权益变动表分析目的与内容
山东理工大学教案 注:教师讲稿附后
第五章所有者权益变动表分析 第一节所有者权益变动表分析目的与内容 一、所有者权益变动表的内涵 1.所有者权益变动表是反映公司本期(年度或中期)内截止期末所有者权益变动情况的报表。 所有者权益是指企业资产扣除负债后由股东享有的“剩余权益”,也称之为净资产,是股东投资资本与经营过程中形成的留存收益的集合,是股东投资和公司发展实力的资本体现。 2.所有者权益变动表一般应单独列报以下项目: 1)净利润; 2)直接计入所有者权益的利得和损失项目及其总额; 3)会计政策变更和会计差错更正的累积影响金额; 4)股东投入资本和向股东分配利润等; 5)按照规定提取的盈余公积; 6)实收资本、资本公积、盈余公积、未分配利润期初和期末余额及其调整情况。 二、编制所有者权益变动表的意义 1.编制所有者权益变动表符合全面收益改革的国际趋势 2.编制所有者权益变动表是公司所有者权益日益受到重视的体现 3.编制所有者权益变动表将更好地为利润表和资产负债表提供辅助信息 4.编制所有者权益变动表能更清晰地体现会计政策变更和前期差错更正对所有者权益的 影响 三、所有者权益变动表分析的目的 所有者权益变动表分析,是通过所有者权益的来源及其变动情况,了解会计期间内影响所有者权益增减变动的具体原因,判断构成所有者权益各个项目变动的合法性与合理性,为报表使用者提供较为真实的所有者权益总额及其变动信息。 所有者权益变动表分析的具体目的如下: 1.通过分析,可以清晰体现会计期间构成所有者权益各个项目的变动规模与结构; 2.通过分析,可以进一步从全面收益角度报告更全面、更有用的财务业绩信息,以满足报表使用者投资、信贷及其他经济决策的需要; 3.通过分析,可以反映会计政策变更的合理性,反映会计差错更正的幅度,具体报告由于会计政策变更和会计差错更正对所有者权益的影响数额; 4. 通过分析,可以反映由于股权分置、股东分配政策、再筹资方案等财务政策对所有者权益的影响。 四、所有者权益变动表的分析内容 第一,所有者权益变动表的水平分析; 第二;所有者权益变动表的垂直分析; 第三,所有者权益变动表的主要项目分析; 第四,管理层相关决策对所有者权益影响的分析。
会计英语资产负债表及利润表
会计报表中英文对照
Accounting
1. Financial reporting(财务报告) includes not only financial statements but also other means of communicating information that relates, directly or indirectly, to the information provided by a business enterprise’s accounting system----that is, information about an enterprise’s resources, obligations, earnings, etc. 2. Objectives of financial reporting: 财务报告的目标 Financial reporting should: (1) Provide information that helps in making investment and credit decisions. (2) Provide information that enables assessing future cash flows. (3) Provide information that enables users to learn about economic resources, claims against those resources, and changes in them. 3. Basic accounting assumptions 基本会计假设 (1) Economic entity assumption 会计主体假设 This assumption simply says that the business and the owner of the business are two separate legal and economic entities. Each entity should account and report its own financial activities. (2) Going concern assumption 持续经营假设 This assumption states that the enterprise will continue in operation long enough to carry out its existing objectives. This assumption enables accountants to make estimates about asset lives and how transactions might be amortized over time. This assumption enables an accountant to use accrual accounting which records accrual and deferral entries as of each balance sheet date. (3) Time period assumption 会计分期假设 This assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods. The most typical time segment = Calendar Year Next most typical time segment = Fiscal Year (4) Monetary unit assumption 货币计量假设 This assumption states that only transaction data that can be expressed in terms of money be included in the accounting records, and the unit of measure remains relatively constant over time in terms of purchasing power. In essence, this assumption disregards the effects of inflation or deflation in the economy in which the entity operates. This assumption provides support for the "Historical Cost" principle. 4. Accrual-basis accounting 权责发生制会计 5. Qualitative characteristics 会计信息质量特征 (1) Reliability 可靠性 For accounting information to be reliable, it must be dependable and trustworthy. Accounting information is reliable to the extend that it is: Verifiable: means that information has been objectively determined, arrived at, or created. More than one person could consider the facts of a situation and reach a similar conclusion. Representationally faithful: that something is what it is represented to be. For example, if a machine is listed as a fixed asset on the balance sheet, then the company
会计报表术语中英文对照
会计报表术语中英文对照、损益表INCOME STATEMENT Op erat ing Results 经营业绩 Gross revenues总收入/毛收入 Net revenues销售收入/净收入 Sales销售额 Turno ver营业额 Cost of revenues 销售成本 Gross profit 毛利润 Gross margin 毛利率 EBITDA息、税、折旧、摊销前利润(EBITDA EBITDA margin EBITD率 EBITA息、税、摊销前利润 EBIT息税前利润/营业利润 Op erat ing p rofit 营业利润 Op erati ng margin营业利润率 EBIT margin EBI■率(营业利润率) Profit before dis posal of inv estme nts 出售投资前利润Op erat ing expen ses:营业费用: Research and development costs (R&D)研发费用
marketi ng expen sesSelli ng expen se销肖售费用 Cost of reve nues 营业成本 Selli ng Cost销售成本 Sales and marketi ng expen ses Selli ng and market ing expens销售费用、或销售及市场推广费用 Selling and distribution costs 营销费用/行销费用 General and administrative expenses 管理费用/一般及管理费用 Admi nistrative expen ses 管理费用 Profit from op erat ing activities营业利润/经营活动之利润 Finance costs财务费用/财务成本 Finan cial result 财务费用 Change in fair value of derivative liability associated with Series B conv ertible redeemable preferenee shares可转换可赎回优先股B相关衍生负债公允值变动 Equity loss of affiliates 子公司权益损失 Profit before tax 税前利润 taxes税项 Profit for the period 本期利润 Net loss净损失 Net Margin净利率 extraord inary gai n and loss 特别损益、非常损益 Gai n on trad ing securities 交易证券收益
所有者权益变动表格式及其内容填写
一般企业所有者权益变动表的列报方法 1.所有者权益变动表各项目的列报说明 (1)“上年年末余额”项目,反映企业上年资产负债表中实收资本(或股本)、资本公积、盈余公积、未分配利润的年末余额。 (2)“会计政策变更”和“前期差错更正”项目,分别反映企业采用追溯调整法处理的会计政策变更的累积影响金额和采用追溯重述法处理的会计差错更正的累积影响金额。为了体现会计政策变更和前期差错更正的影响,企业应当在上期期末所有者权益余额的基础上进行调整得出本期期初所有者权益,根据“盈余公积”、“利润分配”、“以前年度损益调整”等科目的发生额分析填列。 (3)“本年增减变动额”项目分别反映如下内容: ①“净利润”项目,反映企业当年实现的净利润(或净亏损)金额,并对应列在“未分配利润”栏。 ②“其他综合收益”项目,反映企业当年根据企业会计准则规定未在损益中确认的各项利得和损失扣除所得税影响后的净额,并对应列在“资本公积”栏。 ③“净利润”和“其他综合收益”小计项目,反映企业当年实现的净利润(或净亏损)金额和当年计入其他综合收益金额的合计额。 ④”所有者投入和减少资本”项目,反映企业当年所有者投入的资本和减少的资本其中:“所有者投入资本”项目,反映企业接受投资者投入形成的实收资本(或股本)和资本溢价或股本溢价,并对应列在”实收资本”和”资本公积”栏。“股份支付计入所有者权益的金额”项目,反映企业处于等待期中的权益结算的股份支付当年计入资本公积的金额,并对应列在”资本公积”栏。 ⑤“利润分配”下各项目,反映当年对所有者(或股东)分配的利润(或股利)金额和按照规定提取的盈余公积金额,并对应列在“未分配利润”和“盈余公积”栏。其中: “提取盈余公积”项目,反映企业按照规定提取的盈余公积。 “对所有者(或股东)的分配”项目,反映对所有者(或股东)分配的利润(或股利)金额。 ⑥“所有者权益内部结转”下各项目,反映不影响当年所有者权益总额的所有者权益各组成部分之间当年的增减变动,包括资本公积转增资本(或股本)、盈余公积转增资本(或股本)、盈余公积弥补亏损等项金额。为了全面反映所有者权益各组成部分的增减变动情况,所有者权益内部结转也是所有者权益变动表的重要组成部分,主要指不影响所有者权益总额、所有者权益的各组成部分当期的增减变动。其中: “资本公积转增资本(或股本)”项目,反映企业以资本公积转增资本或股本的金额。 “盈余公积转增资本(或股本)”项目,反映企业以盈余公积转增资本或股本的金额。
ACCA F3 中英文单词对照表
第一章 1.资产asset 2.负债liability 3.所有者权益equity=capital=net asset 4.收入income=revenue=sales 5.费用expense 6.厂房plant 7.机器machine 8.无形资产intangible asset 9.非流动资产Non current asset(6 7 8属于9)10.库存现金petty cash 11.银行存款cash 12.应收账款trade receivable=A/R 13.存货inventory 14.流动资产current asset (10 11 12 13属于14)15.贷款loan 16.应付账款trade payables=A/P 17.预收账款advance from customers 18.流动负债current liability(15 16 17属于18)19.实收资本share capital 20.资本公积share premium 21.留存收益Retained earnings=R/ES 22.资产负债表statement of financial position=SOFP 23.所有者权益变动表statement of changes in equity=SOCIE 24.现金流量表statement of cash flow 25.利润表statement of comprehensive income=SOCI 第二章 1.复式记账double-entry bookkeeping 2. 借Debit 3. 贷Credit 4. 预付账款prepayment 5. 利润profit 第四章 1.增值税value added tax=sales tax 2.进项税额input tax 3.销项税额output tax 4.贸易折扣(商业折扣)trade discount 5.现金折扣cash discount 6. 不含税exclusive 7. 含税inclusive 8. 交易事项Transaction 9. 取走withdraw 第五章 1.现金petty cash=cash on hand
会计报表中英文对照
会计报表中英文对照?
Accounting 1. Financial reporting(财务报告) includes not only financial statements but also other means of communicating information that relates, directly or indirectly, to the information provided by a business enterprise's accounting system----that is, information about an enterprise's resources, obligations, earnings, etc. 2. Objectives of financial reporting: 财务报告目标 Financial reporting should:
(1) Provide information that helps in making investment and credit decisions. (2) Provide information that enables assessing future cash flows. (3) Provide information that enables users to learn about economic resources, claims against those resources, and changes in them. 3. Basic accounting assumptions 基本会计假设 (1) Economic entity assumption 会计主体假设 This assumption simply says that the business and the owner of the business are two separate legal and economic entities. Each entity should account and report its own financial activities. (2) Going concern assumption 持续经营假设 This assumption states that the enterprise will continue in operation long enough to carry out its existing objectives. This assumption enables accountants to make estimates about asset lives and how transactions might be amortized over time. This assumption enables an accountant to use accrual accounting which records accrual and deferral entries as of each balance sheet date. (3) Time period assumption 会计分期假设 This assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods. The most typical time segment = Calendar Year Next most typical time segment = Fiscal Year (4) Monetary unit assumption 货币计量假设 This assumption states that only transaction data that can be expressed in terms of money be included in the accounting records, and the unit of measure remains relatively constant over time in terms of purchasing power. In essence, this assumption disregards the effects of inflation or deflation in the economy in which the entity operates. This assumption provides support for the Historical Cost principle. 4. Accrual-basis accounting 权责发生制会计 5. Qualitative characteristics 会计信息质量特征 (1) Reliability 可靠性 For accounting information to be reliable, it must be dependable and trustworthy. Accounting information is reliable to the extend that it is: Verifiable: means that information has been objectively determined, arrived at, or created. More than one person could consider the facts of a situation and reach a similar conclusion. Representationally faithful: that something is what it is represented to be. For example, if a machine is listed as a fixed asset on the balance sheet, then the company can prove that the machine exists, is owned by the company, is in working condition, and is currently being used to support the revenue generating activities of the company. Neutral: means that information is presented in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and practices, and without bias. (2) Relevance 相关性
- ACCA F3 中英文单词对照表
- 最新acca f3 中英文单词对照表学习资料
- 会计英语-单词表 谷丰
- 会计英语资产负债表及利润表
- ACCAF中英文单词对照表
- accaf3中英文单词对照表
- acca f 中英文单词对照表
- 财务报表各项目中英文对照
- (完整版)所有者权益变动表(英文对照)
- Statement of Stockholders equity 所有者权益变动表 英文
- ACCAF中英文单词对照表
- ACCAF3中英文单词对照表
- 中英文对照财务报表常用单词
- 所有者权益变动表英文对照
- 所有者权益变动表英文对照
- 所有者权益(或股东权益)增减变动表中英文对照
- 中英文对照财务报表常用单词
- 常用会计名词(中英文对照)
- 所有者权益变动表(英文对照)
- 所有者权益变动表(中英文)
