A Bibliographic Analysis of the IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems Literature

A Bibliographic Analysis of the IEEE
T RANSACTIONS ON I NTELLIGENT
T RANSPORTATION S YSTEMS Literature Linjing Li,Xin Li,Member,IEEE,Zhenjiang Li,Daniel Dajun Zeng,Senior Member,IEEE,and
William T.Scherer,Member,IEEE
Abstract—This paper presents a bibliographic analysis of the
papers published in the IEEE T RANSACTIONS ON I NTELLI-GENT T RANSPORTATION S YSTEMS(T-ITS).We identify the most productive and high-impact authors,institutions,and countries/
regions.We?nd that research on intelligent transportation sys-
tems is dominated by U.S.researchers and institutions and that
China and Japan are the second most productive countries.
According to this analysis,M.M.Trivedi,N.P.Papanikolopoulos,
and P.A.Ioannou are the three most productive and in?uential
authors in the IEEE T-ITS,whereas the Massachusetts Institute of
Technology,Cambridge,the University of California,San Diego,
and the University of Minnesota,Minneapolis,are three of the
most productive and in?uential institutions in the IEEE T-ITS.
Index Terms—Bibliographic analysis,impact,intelligent trans-
portation systems(ITS),productivity.
I.I NTRODUCTION
I NTELLIGENT transportation systems(ITS)refers to
utilizing synergistic technologies and system engineering methods to develop and improve transportation systems of all kinds[1].Due to the close relationship between transportation systems and our daily life and the economy,studies on ITS have a wide range of critical applications,such as increasing trans-portation safety and convenience(e.g.,automatic driving),im-proving transportation ef?ciency(e.g.,reducing congestions),
Manuscript received March11,2010;revised May1,2010;accepted May4,2010.Date of current version May25,2010.This work was sup-ported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant60621001,Grant70890084,Grant90924302,and Grant90920305; by the Ministry of Science and Technology under Grant2006CB705500and Grant2006AA010106;by the Chinese Academy of Sciences under Grant 2F08N03and Grant2F07C01;and by the City University of Hong Kong under Grant7200170.The Associate Editor for this paper was N.N.Zheng.
L.Li and Z.Li are with the Key Laboratory of Complex Systems and Intelli-gence Science,Institute of Automation,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100190,China(e-mail:linjing.li.cas@https://www.wendangku.net/doc/7f13118949.html,;lzjwhb@https://www.wendangku.net/doc/7f13118949.html,).
X.Li is with the Department of Information Systems,City University of Hong Kong,Kowloon,Hong Kong(e-mail:Xin.Li@https://www.wendangku.net/doc/7f13118949.html,.hk).
D.D.Zeng is with the Key Laboratory of Complex Systems and Intel-ligence Science,Institute of Automation,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing100190,China,and also with the Department of Management Information Systems,University of Arizona,Tucson,AZ85721USA(e-mail: zeng@https://www.wendangku.net/doc/7f13118949.html,).
W.T.Scherer is with the Department of Systems and Information Engineering,University of Virginia,Charlottesville,V A22904USA(e-mail: wts@https://www.wendangku.net/doc/7f13118949.html,).
Color versions of one or more of the?gures in this paper are available online at https://www.wendangku.net/doc/7f13118949.html,.
Digital Object Identi?er10.1109/TITS.2010.2049890and making environmentally friendly transportation solutions (e.g.,fuel consumption reduction)[2].
The IEEE T RANSACTIONS ON I NTELLIGENT T RANS-PORTATION S YSTEMS(T-ITS)has focused on publishing ad-
vances and innovations in the ITS?eld since its launch in 2000.Although it is one of the youngest journals in the IEEE publication family[3],it now has the highest impact factor (2.844in2008[4],[5])among all journals in the transportation sector of the Thomson ISI SCI database and has ambition to achieve more success[5].The ten-year history of the IEEE T-ITS re?ects the development of the ITS?eld.Analyzing its publications can help us assess the productive and high-impact authors,institutions,and regions in worldwide ITS research. In this paper,we employ bibliographic analysis to assess the publication and citation patterns of IEEE T-ITS research papers. Section II explains our methodology,Section III presents the ?ndings from the analysis,and Section IV summarizes our ?ndings.
II.M ETHODOLOGY
We downloaded the metadata for all IEEE T-ITS publications from IEEE Xplore,including title,abstract,authors,author af?liations,references,and keywords.In this research,we con-sider only research papers,including original research papers, reviews,and letters.Editorials,therefore,were excluded from this research,except for guest editorials for Special Issues since 2006,which summarized the recent research status and indi-cated future research directions.To assess the impact of these papers,we downloaded citation information,during March 2010,from the Thomson ISI SCI-E database,which is one of the most comprehensive citation repositories in the world. (Note that the ISI SCI-E database does not include the18T-ITS papers published in2000.)
Initially,we preprocessed the collected data for bibliographic analysis by identifying authors based on their full names and af-?liations and made an effort to align authors with multiple af?l-iations so that their contributions would not be underestimated. Multiple af?liations were still considered separately when as-sessing contributions of institutions and countries/regions.
To measure the productivity of authors,institutions,and countries/regions,we employed the adjusted productivity score (APS)introduced in[6].For a paper with n authors,the APS credits each author1/n of the paper.The APS of an author is the sum of all such credits of all his/her publications.The APS
1524-9050/$26.00?2010IEEE
TABLE I
S TATISTICS OF T-ITS P UBLICATIONS IN THE D ATA S ET
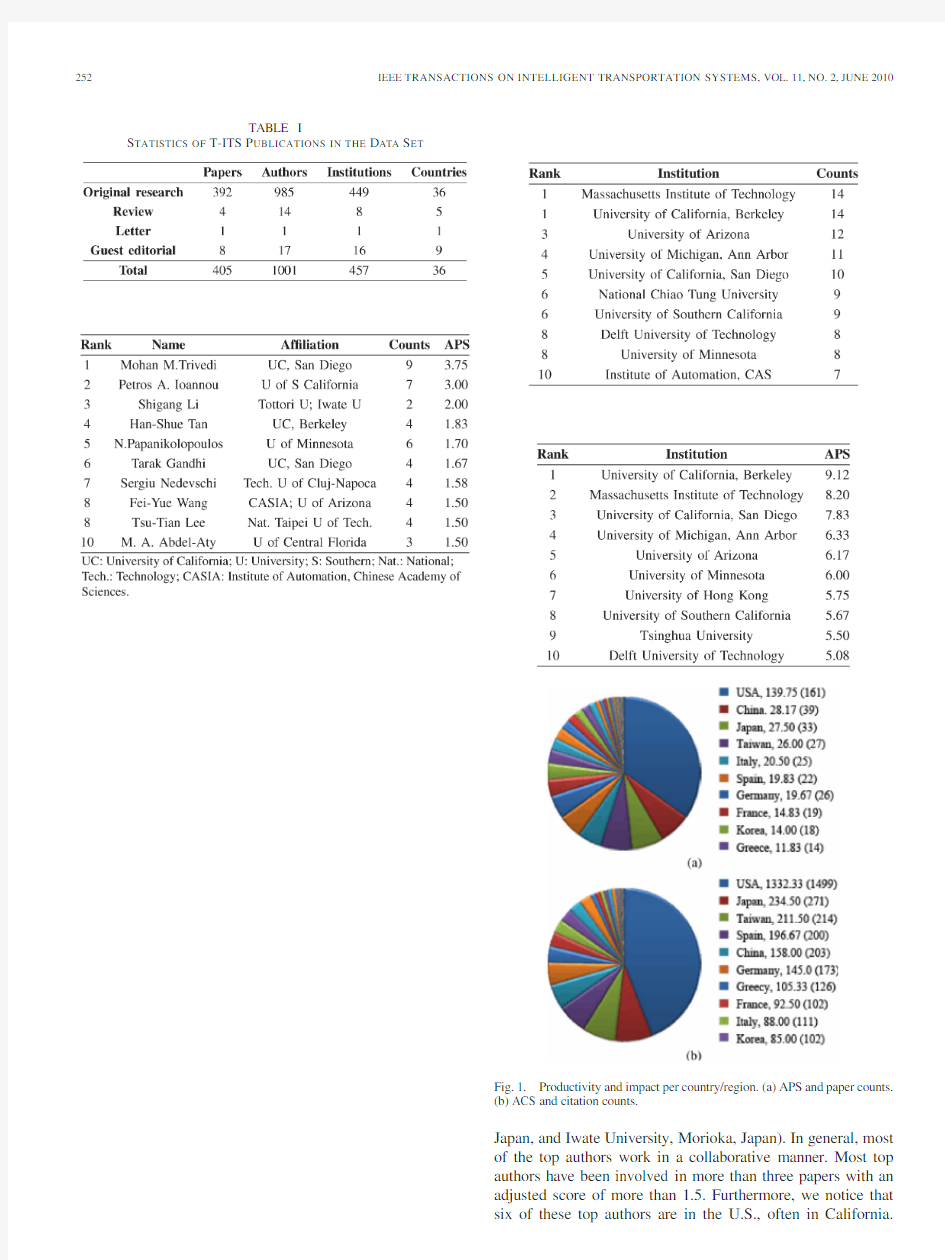
Fig.1.Productivity and impact per country/region.(a)APS and paper counts.
(b)ACS and citation counts.
Japan,and Iwate University,Morioka,Japan).In general,most
of the top authors work in a collaborative manner.Most top
authors have been involved in more than three papers with an
adjusted score of more than1.5.Furthermore,we notice that
six of these top authors are in the U.S.,often in California.
LI et al.:BIBLIOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF THE IEEE T RANSACTIONS ON I NTELLIGENT T RANSPORTATION S YSTEMS LITERATURE253
TABLE V
M OST C ITED P APERS IN THE IEEE T-ITS
254IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS,VOL.11,NO.2,JUNE2010 TABLE VII
M OST C ITED I NSTITUTIONS(T OP T EN)
Linjing Li received the B.Eng.degree in elec-
trical engineering and automation and the M.Eng.
degree in control theory and control engineering
from Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin,China,
in2005and2007,respectively.He is currently work-
ing toward the Ph.D.degree with the Key Laboratory
of Complex Systems and Intelligence Science,Insti-
tute of Automation,Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Beijing,China.
His research interests include game theory,mech-
anism design,auction theory,and machine learning.
Xin Li(S’07–M’10)received the B.Eng.and M.Eng.
degrees in control theory and control engineering
from Tsinghua University,Beijing,China,and the
Ph.D.degree in management information systems
from the University of Arizona,Tucson.
He is currently an Assistant Professor with the De-
partment of Information Systems,City University of
Hong Kong,Kowloon,Hong Kong.His research in-
terests include business intelligence,social network
analysis,data mining,and text mining.
Dr.Li is a member of the Association for Com-
puting Machinery and Association for Information Systems.
LI et al.:BIBLIOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF THE IEEE T RANSACTIONS ON I NTELLIGENT T RANSPORTATION S YSTEMS LITERATURE
255
Zhenjiang Li received the B.Eng.degree in elec-trical engineering and automation from Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing,China,in 2002and the Ph.D.degree in control theory and control engi-neering from the Institute of Automation,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing,in 2007.
He is currently an Assistant Professor with the Key Laboratory of Complex Systems and Intelligence Science,Institute of Automation,Chinese Academy of Sciences.His research interests include agent-based control,parallel control,and management for
transportation.
Daniel Dajun Zeng (S’99–M’04–SM’07)received the M.S.and Ph.D.degrees in industrial ad-ministration from Carnegie Mellon University,Pittsburgh,PA.
He is currently an Associate Professor and a Honeywell Fellow with the Department of Manage-ment Information Systems,University of Arizona,Tucson,and a Research Professor with the Key Laboratory of Complex Systems and Intelligence Science,Institute of Automation,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing,China.His research interests
include software agents and their applications,security informatics,social com-puting,computational game theory,recommender systems,and spatiotemporal data analysis.
Dr.Zeng is the Vice President for the Technical Activities of the IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems
Society.
William T.Scherer (M’87)received the Ph.D.degree in systems engineering from the University of Virginia,Charlottesville,in 1986.
He is currently a Professor with the Department of Systems and Information Engineering,University of Virginia.His research interests include scheduling systems,decision analysis,intelligent systems,com-binatorial optimization,Markov decision processes,and intelligent transportation systems.
Dr.Scherer has served as the President of the IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Society.
